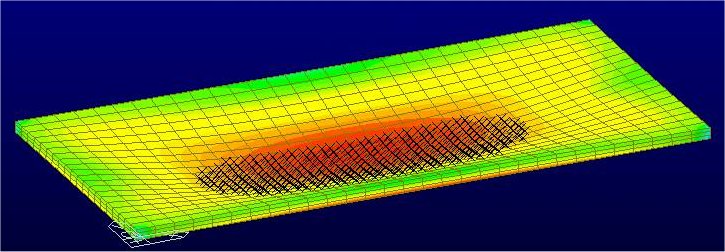
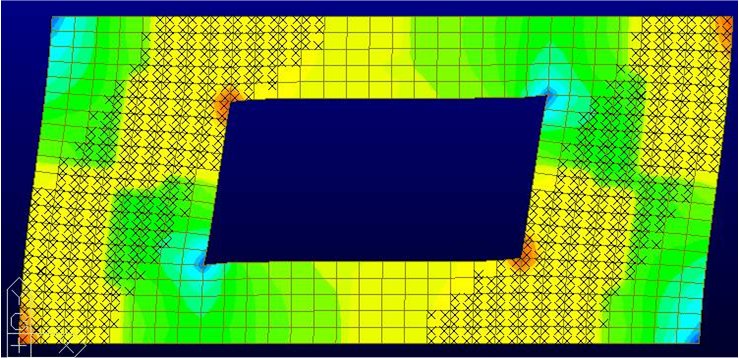
Solid Stresses
Check the stress distribution of solid elements in Contours. Analysis results (stresses) for Moving Load Analysis can be now produced fron the version V610.
From the Main Menu select Results > Results > Stresses > Solid Stresses.
|
 Components
Components
Refer to Figures (a) and (b).
Select the desired stress component among the following :
For UCS
Sig-XX: Axial stress in GCS X-direction
Sig-YY: Axial stress in GCS Y-direction
Sig-ZZ: Axial stress in GCS Z-direction
Sig-XY: Shear stress along the GCS Y-direction in the plane perpendicular to the GCS X-axis
Sig-YZ: Shear stress along the GCS Z-direction in the plane perpendicular to the GCS Y-axis
Sig-XZ: Shear stress along the GCS Z-direction in the plane perpendicular to the GCS X-axis
Sig-P1: Principal stress in the 1st principal axis direction
Sig-P2: Principal stress in the 2nd principal axis direction
Sig-P3: Principal stress in the 3rd principal axis direction
Max-Shear: Maximum shear stress (Tresca Stress)
Sig-EFF: Effective stress (von-Mises Stress)
Sig-Pmax: Display the maximum numerical value among the absolute values of Sig-P1, Sig-P2 and Sig-P3
For Local
Sig - xx: Axial stress in the element's local x-direction (Perpendicular to local y-z plane)
Sig - yy: Axial stress in the element's local y-direction (Perpendicular to local x-z plane)
Sig - zz: Axial stress in the element's local z-direction (Perpendicular to local x-y plane)
Sig - xy: Shear stress along the local y-direction of element in the plane perpendicular to the local x-axis of element
Sig - yz: Shear stress along the local z-direction of element in the plane perpendicular to the local y-axis of element
Sig - xz: Shear stress along the local z-direction of element in the plane perpendicular to the local x-axis of element
Vector: Display the principal stresses in 3 principal axis directions in vectors
Vector Scale Factor: Drawing scale for the vector diagram
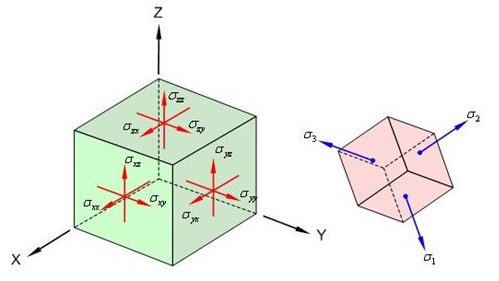
(a) Axial and Shear Stress Components (b) Principal Stress Components
 Type of Display
Type of Display
Define the type of display as follows:
|
Contour |
Display the stresses of solid elements in contour.
|
|
|
Ranges: Define the contour ranges.
Note Number of Colors: Assign the number of colors to be included in the contour (select among 6, 12, 18, 24 colors) Colors: Assign or control the colors of the contour. Color Table: Assign the type of Colors.
Reverse Contour: Check on to reverse the sequence of color variation in the contour. Contour Line: Assign the boundary line color of the contour Element Edge: Assign the color of element edges while displaying the contour Contour Options: Specify options for contour representation Contour Fill Gradient Fill: Display color gradient (shading) in the contour. Draw Contour Line Only Mono line: Display the boundaries of the contour in a mono color. Contour Annotation Spacing: Specify the spacing of the legend or annotation. Coarse Contour (faster) (for large plate or solid model) Extrude
|
|
Deform |
Display the deformed shape of the model.
|
|
|
Deformation Scale Factor Beam Deformation Nodal Deform: Display the deformed shape only with nodal displacements. Real Displacement (Auto-Scale off): The true deformation of the structure is graphically represented without magnifying or reducing it. This option is typically used for geometric nonlinear analysis reflecting large displacement. Relative Displacement: The deformation of the structure is graphically represented relative to the minimum nodal displacement, which is set to "0"
|
|
Values |
Display the stresses of solid elements in numerical values. |
|
|
Decimal Points: Assign decimal points for the displayed numbers. Min & Max: Display the maximum and minimum values. Set Orientation: Display orientation of numerical values. Note
|
|
Legend |
Display various references related to analysis results to the right or left of the working window.
|
|
|
Legend Position: Position of the legend in the display window Rank Value Type: Specify a type of values in the Legend and the number of decimal points.
|
|
Animate |
Dynamically simulate the stresses of the solid elements.
|
|
|
Animation Mode: Determine the type of animation for analysis results. Animate Contour: Option to change the color of the contour representing the transition according to the magnitudes of variation Note AVI Options: Enter the options required to produce the animation window. Bits per Pixel: Number of bits per pixel to create the default window for animation Construction Stage Option: Select the animation options when the construction stage analysis is performed. Stage Animation: Animations by construction stages |
|
Undeformed |
Overlap the undeformed and deformed shapes of the model.
|
|
Mirrored |
"Mirrored" allows the user to expand the analysis results obtained from a half or quarter model into the results for the full model by reflecting planes.
|
|
|
Half Model Mirroring
|
|
Yield Point |
If the analysis results produced by material nonlinear analysis exceed the yield stress of Plastic Material defined in Initial Uniaxial Yield Stress, Hinge is produced at Gauss Point. |
[Check the results obtained from the analysis of masonry materials]
|
Cutting Plane |
Graphically display the stresses of the solid elements along a cutting plane.
|
|
|
Click
|
|
Named Planes for Cutting Outline Type Free Face: Draw the outline of all the faces that are not in contact with other solid elements.
Animation Option Global X Sweep: Produce a stress contour animation for the cut plane by moving the cutting plane toward GCS X-direction |
|
IsoSurface |
IsoSurface searches and displays the planes of equal stresses resulting from Heat of Hydration analysis within the solid elements.
|
|
|
IsoValue Mode Relative(0~1) IsoSurface Values Draw Polygon Outline Model Outline Free Face: Draw the outline of all the faces that are not in contact with other solid elements. Note |
 Batch Output Generation (
Batch Output Generation ( .jpg) ,
, .jpg) )
)
Given the types of analysis results for Graphic outputs, generate consecutively graphic outputs for selected load cases and combinations. A total number of files equal to the products of the numbers of checked items in the three columns of the dialog box below are created.
|
|
Assign a Base File Name under which the types of results (selection data in the Batch Output Generation dialog box for graphic outputs) are stored. |
|
|
Specify the Base Files to perform Batch Output Generation, construction stages, load cases (combinations), steps, etc. in the following dialog box. |
Saved Menu-Bar Info's: Listed here are the Base Files. Select the Base File Names for Batch Output.
![]() : Delete all the Base Files selected with the mouse.
: Delete all the Base Files selected with the mouse.
When the construction stage analysis is carried out, all the construction stages are listed. We simply select the stages of interests to be included in the batch output. If no construction stage analysis is performed, the column in the dialog box becomes inactive and lists load (combination) conditions.
Stages
The results output of all the construction stages are produced. The construction stages are listed below.
Final Stage Loads
The results output for only the Final Stage are produced. The construction stages are listed below. If no construction stage analysis is performed, the load (combination) conditions are listed.
Use Saved
Apply only the (saved) step or load (combination) condition selected at the time of creating each Base File.
Stage LCase/LComb
When the construction stage analysis is carried out, the auto-generated construction stage load conditions and the additionally entered construction stage load combinations are listed. Check on only the load (combination) conditions that will be used to produce batch outputs. This column becomes inactive if "Final Stage Loads" is selected or no construction stage analysis is carried out.
Step Option
Specify the steps for which the outputs will be produced when the construction stage analysis or large displacement geometric nonlinear analysis is performed.
Saved Step: Use only the steps used for creating the Base Files
All Steps: Use all the steps
Output Options
Output File Type
Select a Graphic File type, either BMP or EMF.
Auto Description: At the top left of the Graphic Outputs produced in batch, auto-generate and include the notes such as the types and components of the analysis results, construction stages and steps, load (combination) conditions, etc. The font size, color, type, etc. can be changed upon clicking the button ![]() .
.
Output Path
Specify the path for saving the graphic files to be produced in batch.
File Prefix: Specify the prefix of the Graphic Files to be created. The filenames will be consisted of "Prefix"_"Base File Name"_"Load Comb.".bmp(emf) or "Prefix"_"Base File Name"_"Stage"_"Stage LCase"_"Step".bmp(emf).
![]() : Produce the specified batch Graphic Files reflecting the contents of the dialog box.
: Produce the specified batch Graphic Files reflecting the contents of the dialog box.
![]() /
/ ![]()
Produce the contents of data input in the Base Files and Batch Output Generation dialog box in a binary type file (fn.bog). Click the ![]() button and select a fn.bog to use the same output format.
button and select a fn.bog to use the same output format.
Note
Import /Export is only meaningful for different projects. In a given structural model, the Base Files are automatically stored and listed.