Mesh Common Functions

Construct meshes using the Loop Mesh generating
algorithm.
Quadrilateral
Generate Quadrilateral 2D meshes.
Triangle
Generate Triangular 2D meshes.
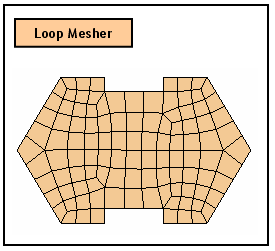
Construct meshes using the Grid Mesh generating
algorithm.
Quad + Tria
Generate 2D meshes using both Quadrilaterals and Triangles.
Triangle
Generate Triangle 2D meshes.
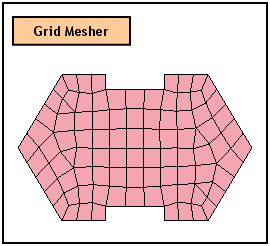
Delaunay Mesher
Construct meshes using the Delaunay
Mesh generating algorithm.
Quadrilateral
Generate 2D meshes using both Quadrilaterals and Triangles.
Quad + Tria
Generate 2D meshes using both Quadrilaterals and Triangles.
Triangle
Generate Triangle 2D meshes.
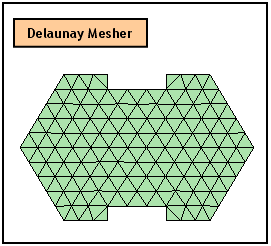
Map Mesher
Construct meshes using the Mapped Mesh generating algorithm.
Quadrilateral
Generate
Quadrilateral 2D meshes.
Triangle
Generate
Triangle 2D meshes.
Backup Mesher
Select
a Backup Mesher, which will be used if a selected face
or the distribution of nodes is inappropriate for Mapped meshing.
Select Corner Vertices
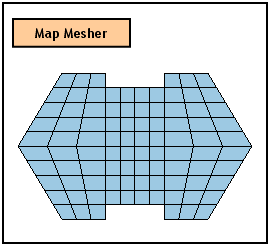
The Mapped Mesh generation algorithm maps a selected shape into squares and creates a square mesh and then maps the mesh created from the original shape. Accordingly, a group of four edges, which will be mapped into each edge of a square, needs to be defined. Four vertices of the edges, which make up the boundaries of a face, are selected. If a face is of an ideal configuration, the program automatically generates Mapped Mesh without having to define corner vertices
Refinement Factor
The size of elements within
the selected shapes is determined. The Fine option
creates a dense mesh while the Coarse option creates a sparse mesh.

Assign
an Attribute ID, which will be assigned to the generated mesh. It can
be specified using previously generated Attribute or creating a new by
clicking button. If user would like to apply the same Attribute
with previously generated Mesh, click button and select a Mesh Set which has the desired Attribute
from the Work Window.
Add to
Register
the generated mesh in a Mesh Set. It can be selected from the Mesh Set
list which is located on the right of 'Add to' or from the Work Window
by using button.
If
'Mesh Set' is selected from the list, a new Mesh Set is registered containing
the generated mesh. The name of a new Mesh Set will be Auto-Mesh(3D) by
default.
As Sub-Set
The new generated mesh becomes registered in a sub Mesh Set of the selected Mesh Set. This option activates when a Mesh Set is selected from the list.
When generating mesh sets
for selected solids, this option will merge nodes at free edges. Nodes
can be merged within a specified tolerance. The
tolerance must be less than 1/10 of the smallest mesh size.
Creates a node in the middle
of each element edge. Consequently, generated element becomes high ordered.
Deletes the Source 2D meshes
after generating mesh.
Hides the object edges
after generating meshes.
Meshes
only the unmeshed faces among the selected faces.
Skips any solid geometry that is unable to generate a solid mesh.
Attempts to generate a linear Mapped-Mesh. If the mesh fails to generate a Mapped-mesh then the processor will revert to auto-meshing the geometry based on the default mesh preference setting.
Refer to Generate Mid-side nodes on map mesh for details.
Matches the connectivity of nodes at the contact face between two solids.
Post Remesh can be set before automeshing. When selected, it improves poor quality mesh from auto meshing. The existing mesh is deleted when the surface is remeshed.
Improves the quality of quadrilateral finite element meshes. Cleans all unused data from all selected mesh objects by improving node connectivity, boundary and flange patterns, quad shape, and to some extent, quad size.
Hides the object faces after generating meshes.
Hides the object solids after generating meshes.
When creating connecting elements, Beta Angle, the coordinates of Reference Point, or Reference Vector are specified to define the orientation of sections.
Beta Angle
Enter
the Beta Angle (β) to identify the orientation of each cross-section.
The Beta Angle relates the ECS to the GCS.
The ECS x-axis starts from the first node and passes
through the second node for all line elements. The ECS
z-axis is defined to be parallel with the direction
of I dimension of cross-sections. That is, the y-axis
is in the strong axis direction. The use of the right-hand rule prevails
in the process.
Ref. Node
If
the coordinates of the Reference Node are entered, it internally computes
the angle of the point and enters the angle as a Beta Angle automatically.
Ref. Vector
If
the coordinates of the Reference Vector are entered, z-axis
of an element is placed on the plane containing the Vector. Clicking button enables to select a vector (Datum
Axis, Datum Plane, Face, Edge) from the Work Window.
Meshed tetra elements that have all nodes lying along the outer boundary edges are considered clamped elements. Using the "Avoid Tetra with All Boundary Nodes" prevents all nodes from lying along the boundary edges.
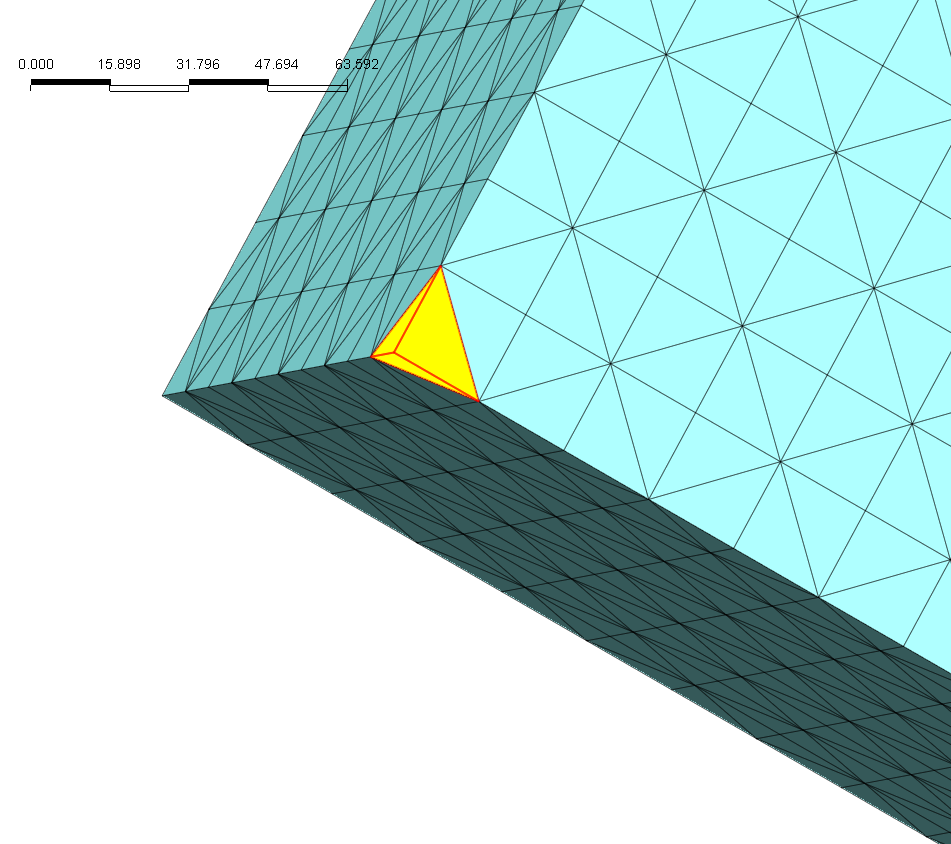
The element highlighted in yellow represents a clamped element. since all 3 nodes are on the boundary edges. To avoid clamped element configuration check on "Avoid Tetra with All Boundary Nodes."