Check Quality

Function
Check Quality provides information of mesh quality.
Call
Mesh > Check Quality
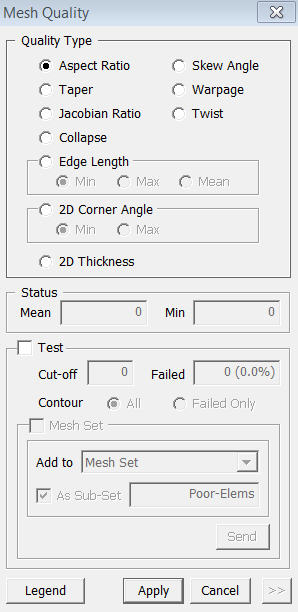
<Check Quality>
Quality Type
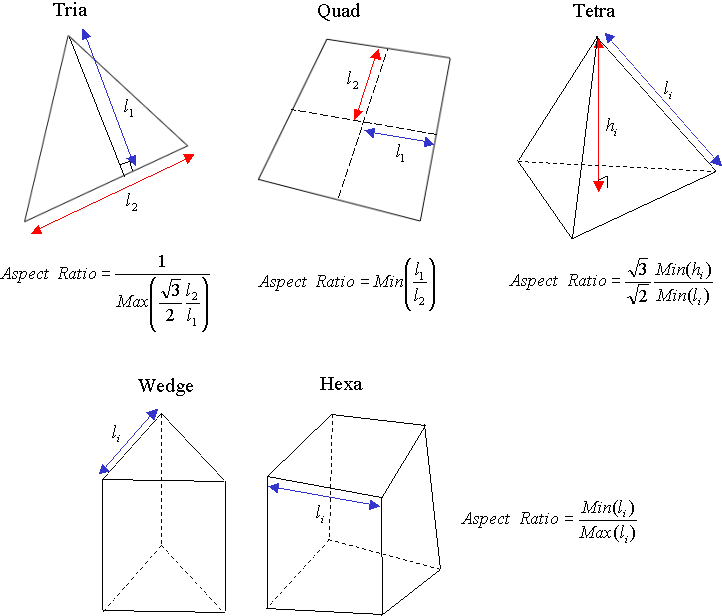
Aspect Ratio
The aspect ratio of 2D element is defined as the ratio of its shortest edge length to its longest edge length. A square has the aspect ratio of 1 since its sides have the same length. As it gets away from the square shape, the aspect ratio becomes smaller than 1.
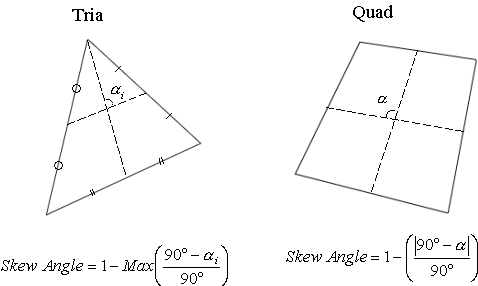
Skew Angle
An angle
is formed by the two lines which pass through the midpoints of the sides
of the quadrilateral.
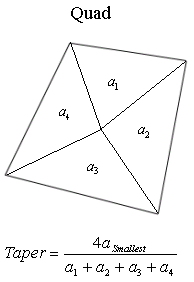
Taper
It checks
for the amount of deviation of the quadrilateral element from a rectangular
shape. A rectangular element has the taper of 1, and it gets away from
the rectangular shape (closer to the triangular shape), the taper becomes
smaller. For the quadrilateral elements, the skew angle is found as shown
in the figure. For solid element (
Warpage
The
warpage of the quadrilateral elements is defined as the deviation from
a best-fit plane that contains the element. It is not always a case to
define a plane with 4 nodes. Therefore, a node of the quadrilateral element
may be formed outside of a plane. The warpage is a measurement how this
node has been deviated, and as it gets closer to 0, the element become
more planar. For the quadrilateral elements, the warpage is found as shown
in the figure. For solid element (
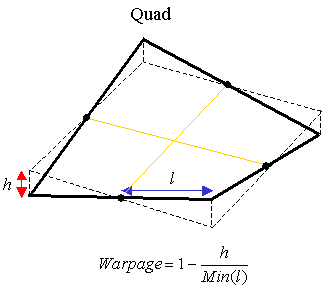
The
If the quadrilateral element is not convex, the negative Jacobian ratio will be obtained, and elements with the negative Jacobian Ratio can not be solved with correct result.
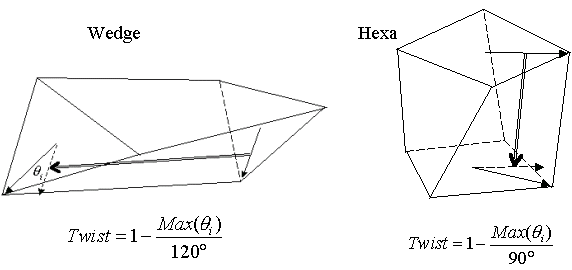
Twist
Twist represents the factor which measures how much two facing element faces are twisted.
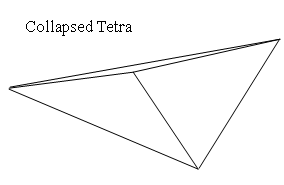
Collapse
When auto-generating a mesh in a complex or invalid geometry. A tetra element, which seems as thin as a planar element, will be often generated. This type of the element is called as a collapsed tetra, and this option enable to check for such a collapsed element.
Edge Length
Check for the length of element edges.
2D Corner Angle
Check
for the corner angle of 2D elements.
2D Thickness
Check for the thickness of plate elements.
Status
Mean
Enter the mean value of the selected mesh quality check.
Enter the minimum value of the selected mesh quality check.
Test
Cut-off
Define
the Cut-off value by which program will find the elements which have a
lower quality value.
Failed
Displays
the number of elements which has a lower quality value than the Cut-off.
Contour
All
Displays
all elements.
Failed only
Displays
only the elements which has a lower quality value than the Cut-off.