 Revision of Ver.7.4.1
Revision of Ver.7.4.1 Revision of Ver.7.4.1
Revision of Ver.7.4.1Function
Enter the isotropic and orthotropic material properties. The user should enter the orthotropic material in User Defined Material.
Call
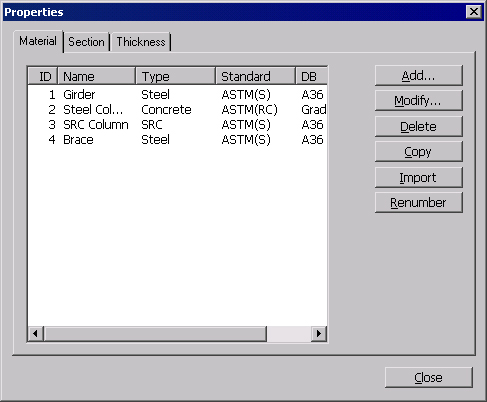
From the Main Menu select Model > Properties > Material.
Select Geometry > Properties > Material in the Menu tab of the Tree Menu.
Click .jpg) Material in the Icon Menu.
Material in the Icon Menu.
Entry
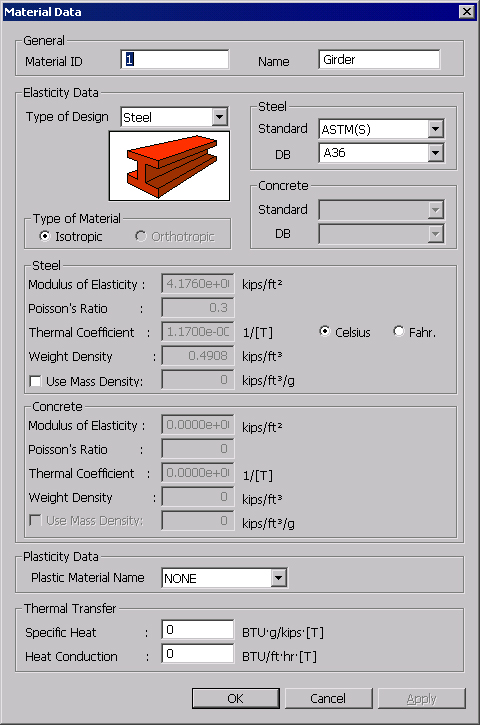
For new or additional material properties
Click in the Properties dialog box and enter the following data:
 General
General
Material ID: Material property number
Name: Material property name
 Revision of Ver.7.4.1
Revision of Ver.7.4.1
 Elasticity
Data
Elasticity
Data
Type of Design: Select a material property type and enter the related data.
Standard: Select the standards of a country in the field.
None: The user defines the material properties directly. The user may modify the data obtained from the DB standards.
ASTM(S): American Society for Testing Materials
CSA(S): Canadian Standards Association
BS(S): British Standard
BS04(S): British Standards / BS EN 10025 (2004)
DIN(S): Deutches Institut fur Normung e.v
EN(S): European Standard
JIS(S): Japanese Industrial Standards
JIS-Civil(S): Japanese Civil Standards
GB03(S): Chinese National Standard
GB(S): Chinese National Standard
JGJ(S): Chinese Industrial Standard
JTJ(S): Chinese National Standard of Highway Engineering
JTG04(S): Chinese Technical Standard of Highway Engineering. Wire and heat treated rebar materials can be selected from DB
TB05(RC): TB 10002.3-2005 (Code for design on reinforced and prestressed concrete structure of railway bridge and culvert)
KS(S): Korean Industrial Standard
KS-Civil(S): Korean Civil Standards
IS(S): Indian Standards
CNS(S): Chinese National Standard
DB: Select a steel type recognized in each of the standard codes.
Standard: Select the standards of a country in the field.
None: The user defines the material properties directly. The user may modify the data obtained from the DB standards.
ASTM(RC): American Society for Testing Materials
CSA(RC): Canadian Standards Association
BS(RC): British Standard
Note
When material data are defined per BS or Chinese Standards, Cubic compressive
strength is used as opposed to Cylinder strength.
EN(RC): European Code
JIS(RC): Japanese Industrial Standards
GB(RC): Chinese National Standard
GB-Civil(RC): Chinese National Standard
JTG04(RC): Chinese Technical Standard of Highway Engineering
TB05(RC): TB 10002.3-2005 (Code for design on reinforced and prestressed concrete structure of railway bridge and culvert)
KS01(RC): Korea Industrial Standards (in SI unit system)
KS(RC): Korean Industrial Standards (in MKS unit system)
KS-Civil(RC): Korean Civil Standards
IS(RC): Indian Standards
CNS(RC): Chinese National Standard
JTG04(S) : Jiao Tongbu Gong Lu Biao Zhun (China)
UNI(RC): Italian National Standards
DB: Select a concrete type recognized in each of the standard codes.
Enter the material properties for steel and concrete in the Steel and Concrete entry windows similar to the above Type = 'Steel', 'Concrete' cases.
Type of Design = 'User Defined'
Select when the material type is not 'Steel',
'RC' or 'SRC', or when the user wishes to define the material properties
directly.
Orthotropic material properties can be also defined in ECS. User Defined
materials are not used in Design.
Modulus of Elasticity
Poisson's
Ratio
Poisson's ratio is used to calculate the Shear Modulus of Elasticity.
Thermal Coefficient
Thermal Coefficient for thermal stress analysis.
Celsius
Fahr
Weight
Density
Use Weight Density to calculate self-weights and masses.
Shear Modulus:
Shear Modulus of Elasticity(Local-xy, Local-xz, Local-yz)
Shear Modulus of Elasticity = Modulus of Elasticity / (2 x (1+Poisson's
ratio))
Note
For Type of Material = Isotropic, Shear Modulus is calculated by the above
expression. For Type of Material = Orthotropic, the user defines the values
of shear modulii.
Use Mass Density: Mass per unit volume.
Note
If "Use Mass Density" is checked, Mass Density is calculated
using the acceleration of gravity(g) given in the DB. If "Use Mass
Density" is unchecked, Mass Density is calculated using the acceleration
of gravity(g) specified in Model>Structure Type. The Mass is separate
from Dead Load and used for eigenvalue analysis only.
 Plasticity
Data
Plasticity
Data
Enter plastic material data.
Plastic Material Name: Select a Plastic Material whose plastic model properties have been defined in the Plastic Material dialog box.
 Thermal
Transfer
Thermal
Transfer
Thermal transfer data
Specific Heat
Heat Conduction
To modify previously entered material property data
Select the material property to be modified in the list of the Properties dialog box and click to modify the related data.
To remove previously entered material property data
Select the material property to be deleted in the list of the Properties dialog box and click .
To copy previously entered material property data
Select the material property to be copied in the list of the Properties dialog box and click .
To import material property data from an existing fn.MGB file
Click .jpg) and select the MGB file
containing the material property data or specify a file name then click
and select the MGB file
containing the material property data or specify a file name then click
.jpg) .
.
Material
List
Display material property data contained in the existing fn.MGB file.
Selected
List
Select material property data to be imported and register them in the Selected
List.
Note
If a fn.MGB is selected, all the material property data contained in the existing fn.MGB
file are registered in the Selected List.
Numbering
Type
Specify the Import mode for material property numbers.
Keep ID.
Import the data keeping the same material property numbers.
New ID.
Assign new numbers to the imported material property data.
To modify previously entered material property numbers
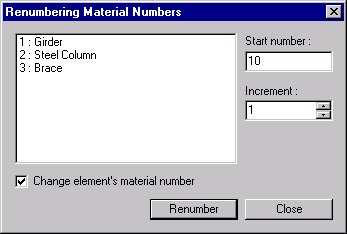
Renumbering Material Number dialog box
Start number
Assign a new starting number for the material to be modified.
Increment
Enter the increment for numbering material property numbers.
Change
element's material number
Modify a material property number. Using this option will modify the previously
defined material property number. If this option is not checked, the selected
material having previously defined number will become undefined and the
additional user-defined material number will be created without any assigned
elements.