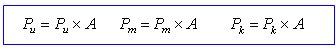Pile Spring Supports | ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
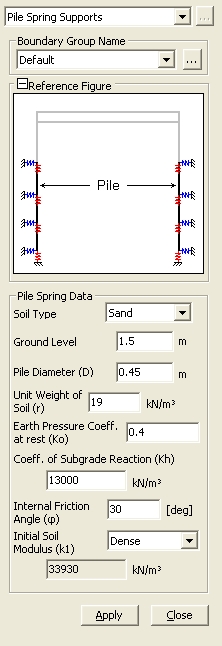
Assign the springs for the soils adjacent to piles. Lateral springs for the soils adjacent to piles are modeled as symmetric nonlinear elastic springs () and vertical springs for the soils adjacent to piles are modeled as linear elastic springs (). The stiffness of soil springs is automatically calculated and entered into Point Spring Supports. The entered data can be checked from Point Spring Supports Table. | ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
From the Main Menu select Model > Boundaries > Pile Spring Supports.
Select Geometry > Boundaries > Pile Spring Supports in the Menu tab of the Tree Menu. | ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
New for V.7.6.1
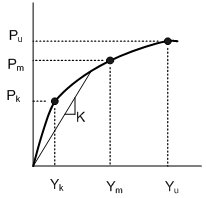
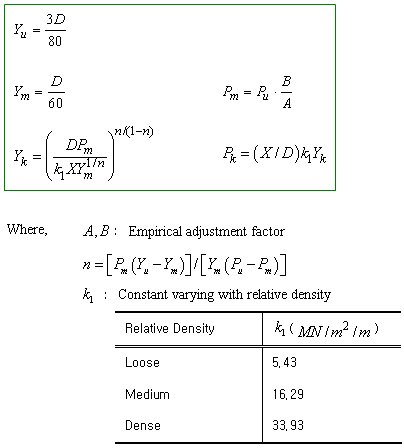
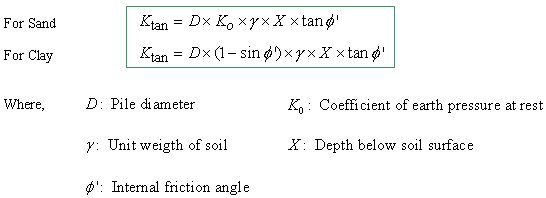
The Stiffness of Nonlinear Elastic (Lateral) Springs for the Soils adjacent to Piles
Calculation of Pu in case of Sand Soil The value of Xt denotes the depth when the following two Pu values are equal. Make the right terms of two equations equal, rearrange the equation in terms of X and solve the quadratic equation.
Calculation of Pu in case of Clay Soil
The final spring stiffness is determined by multiplying the stiffness per unit area calculated above by the area.
The Stiffness of Linear Elastic (Vertical) Springs for the Soils adjacent to Piles
The direction of the linear elastic vertical springs for the soils adjacent to piles should be perpendicular to the ground (GCS '-'Z direction). Even though the piles are not perpendicular to the ground, the z-direction (Node Local Axis) of the nodes for Piles should coincide with the GCS Z-direction. | ||||
|
|