Unknown Load Factor
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use optimization techniques to determine the optimal load factors that satisfy the specific constraints of a structure.
This function optimizes tensions of cables at the initial equilibrium position of a cable structure. The program can calculate the initial cable force by inputting the restrictions such as displacement, moment, etc. and satisfying the constraints. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
From the Main Menu select Results > Unknown Load Factor.
Select Results > Unknown Load Factor in the Menu tab of the Tree Menu. |
|
|
|
|
|
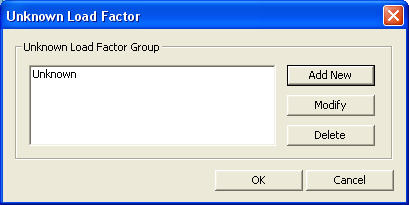
In order to calculate unknown load factors using optimization techniques, load combinations, load cases pertaining to the unknown load factors, specific constraints and object functions are required. All these data are collected in a unique and unknown load factor group for analysis. Several groups can be formulated where they can be saved, modified or deleted.
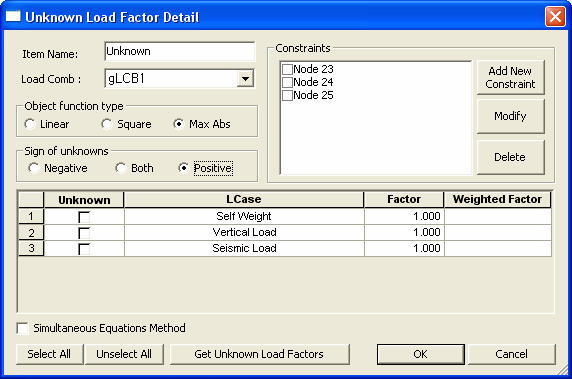
Unknown Load Factor Item Detail dialog box
When a new Unknown Load Factor Group is created by clicking or when a group is modified by clicking , enter or modify the data in Unknown Load Factor Detail shown below.
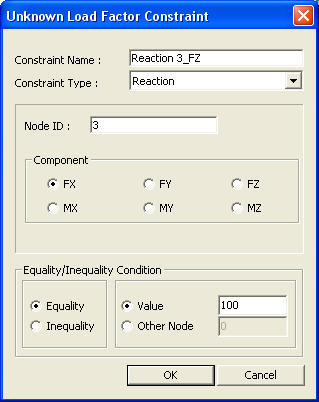
Unknown Load Factor Constraint dialog box
Item Name: Enter the name of the Unknown Load Factor Group.
Load Comb: Select a load combination from the previously entered load combinations in "Results>Combinations" to calculate the unknown load factors. The load combination used to calculate the unknown load factors must include the load cases that form the basis of the load factors.
In the latest version of MIDAS/Gen, the numbers of loads are limited to 150 in each load combination. Therefore, if the load conditions to determine the Unknown Load Factors exceed 150, then the conditions should be divided into two or more combinations, each less than 150 load cases, and each combination should be defined. The load combinations should then be grouped, and the group should be selected as another load combination.
Object Function type: Select the method of forming an object function consisted of unknown load factors.
Linear: The sum of the absolute values of Load factor x weight
Square: The linear sum of the squares of Load factor x weight
Max Abs: The maximum of the absolute values of Load factor x weight
Sign of Unknowns: Assign the sign of the unknown load factors to be calculated.
Negative: Limit the range of the calculated values to the negative (-) field.
Both: Do not limit the range of the calculated values.
Positive: Limit the range of the calculated values to the positive (+) field.
Unknown: Check in the load case for which the unknown load factor is to be obtained. When load cases are activated as unknown load factors, the character "Unknown" appears in the Factor field of the relevant load case.
LCase: The name of the load case to be used as an unknown load factor.
Weighted Factor: Weighted Factors are scale factors that control the relative importance of the unknown load factors in the object functions.
Constraints: Enter the constraints to be satisfied by the load combination results that include the unknown load factors. When specifying the constraints, a list of constraints is created. The constraints may be selectively applied. The constraint types are displacement, reaction and member force for the truss or beam element.
: Select to create a new constraint.
: Select to modify a previously entered constraint.
: Select to delete a previously entered constraint.
When or is selected.
Constraint Name: Specify the constraint name
Constraint Type: Specify the constraint type
Unknown Load Factor Constraint dialog box
Node ID: Enter the constrained node number.
Component: Select a displacement component from the 6 degrees-of-freedom.
Equality/Inequality Condition
Equality: Condition where the value of the reaction in the load combination that includes the unknown load factors (or the reaction value of the relevant component of another node) is equal to the entered value
Value: Enter the reaction component value that must be satisfied by the load combination that includes the unknown load factors.
Other Node: The reaction of another node for the specified component, entered in the load combination, is imposed to the Node ID.
Inequality: Where the value of the reaction in the load combination that includes the unknown load factors is between the Upper Bound and the Lower Bound, you may enter both Upper Bound and Lower Bound or either of them.
Upper Bound: Upper limit of the condition
Lower Bound: Lower limit of the condition
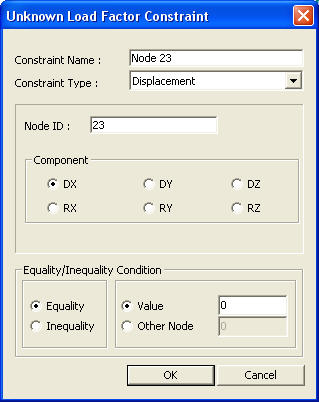
Unknown Load Factor Constraint dialog box
Node ID: Enter the constrained node number.
Component: Select a reaction component from the 6 degrees-of-freedom.
Equality/Inequality Condition
Equality: Condition where the value of the displacement in the load combination that includes the unknown load factors (or the displacement value of the relevant component of another node) is equal to the entered value
Value: Enter the displacement component value that must be satisfied by the load combination that includes the unknown load factors.
Other Node: The nodal displacement of another node for the specified component, entered in the load combination, is imposed to the Node ID.
Inequality: Where the value of the displacement in the load combination that includes the unknown load factors is between the Upper Bound and the Lower Bound, you may enter both Upper Bound and Lower Bound or either of them.
Upper Bound: Upper limit of the condition
Lower Bound: Lower limit of the condition
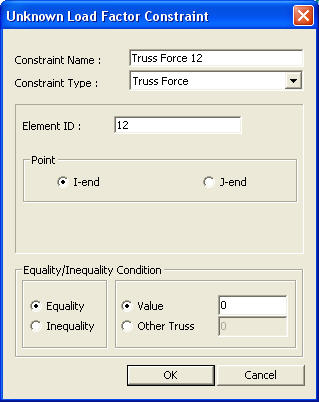
Unknown Load Factor Constraint dialog box
Element ID: Enter the constrained truss element number.
Component: Select one end of the member for force constraint.
Equality/Inequality Condition
Equality: Condition where the value of the truss element's member force in the load combination that includes the unknown load factors (or the member force value of another truss element) is equal to the entered value
Value: Enter the truss element's member force value that must be satisfied by the load combination that includes the unknown load factors.
Other Truss: The member force of another truss, entered in the load combination, is imposed to the Element ID.
Inequality: Where the value of the truss element's member force in the load combination that includes the unknown load factors is between the Upper Bound and the Lower Bound, you may enter both Upper Bound and Lower Bound or either of them.
Upper Bound: Upper limit of the condition
Lower Bound: Lower limit of the condition
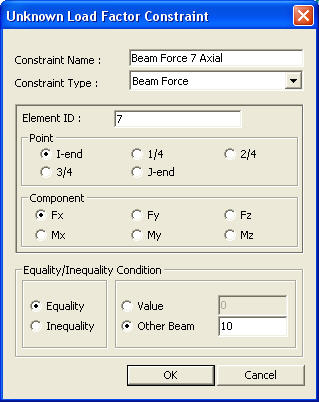
Unknown Load Factor Constraint dialog box
Element ID: Enter the constrained beam element number.
Point: Select a point along the length of the member for force constraint.
Component: Select a component of the member forces.
Equality/Inequality Condition
Equality: Condition where the value of the beam element's member force in the load combination that includes the unknown load factors (or the member force value of another beam element) is equal to the entered value
Value: Enter the beam element's member force value that must be satisfied by the load combination that includes the unknown load factors.
Other Beam: The member force of another beam, entered in the load combination, is imposed to the Element ID.
Inequality: Where the value of the beam element's member force in the load combination that includes the unknown load factors is between the Upper Bound and the Lower Bound, you may enter both Upper Bound and Lower Bound or either of them.
Upper Bound: Upper limit of the condition
Lower Bound: Lower limit of the condition
Simultaneous Equation Method: If all the selected constraints are Equality Type, and the number of constraints and unknown loads are also equal, then this option can be selected. In this case, the program will determine the unknowns by combining the equations without using the optimization technique.
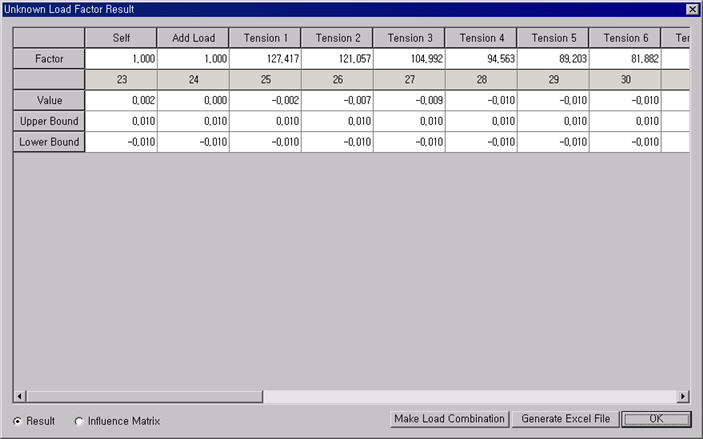
The program calculates the magnitudes of the selected Unknown Load Factor groups, which minimize the object functions, using the given constraints. The results are as follows:
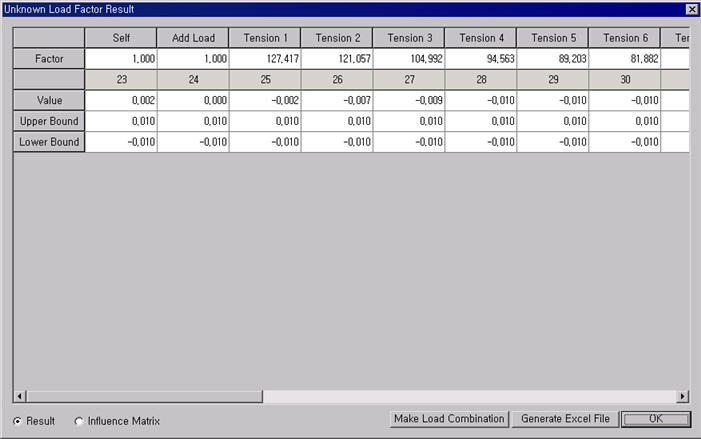
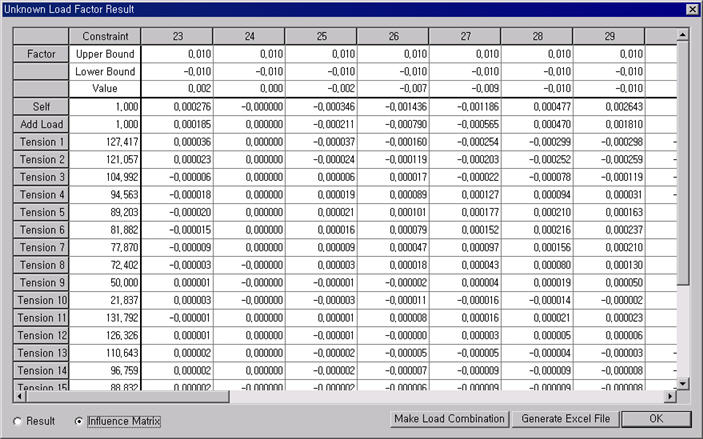
Unknown Load Factor Result
Factor: Calculated unknown load factors
Value: Resulting values of the constraints
Upper Bound: Upper bound of each constraint
Lower Bound: Lower bound of each constraint
Influence Matrix: The calculated results of Unknown Load Factors are produced including Influence Matrix.
Unknown Load Factor Result including Influence Matrix
Make Load Combination dialog box
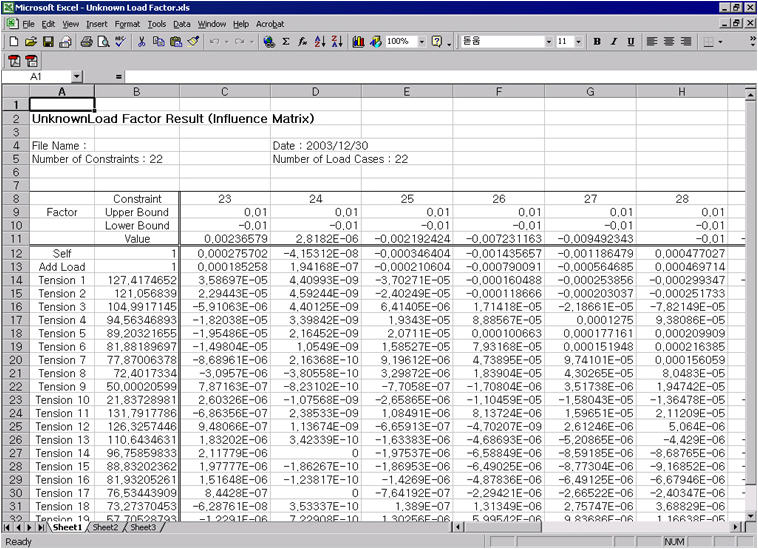
The calculated results of Unknown Load Factors including Influence Matrix are produced in an Excel file.
Results of Unknown Load Factors converted into an Excel fileNote
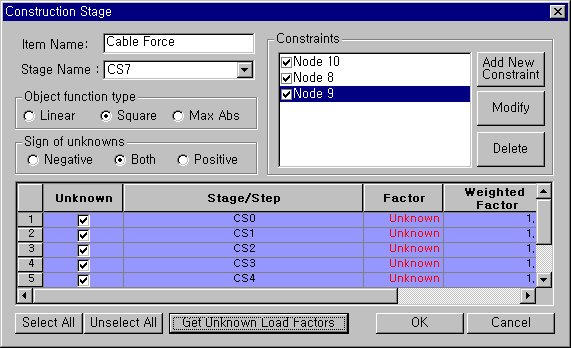
Functionality of Unknown Load Factor considering construction stage
Item Name Specify a group name representing the unknown load factors.
Stage Name Select a Construction Stage for which unknown load factors will be calculated.
Note
This tab performs an iterative analysis to calculate the Unknown Load Factor for each construction stage.
For a case considering the creep when calculating
the cable forces of a Cable-Stayed Bridge during construction, since creep
occurs due to the cable force, the most optimum cable force during construction
cannot be calculated in one analysis. In this case there should be an
iterative process to optimize the cable force. By clicking
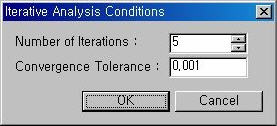
Unknown Load Factor iterative analysis dialogue box
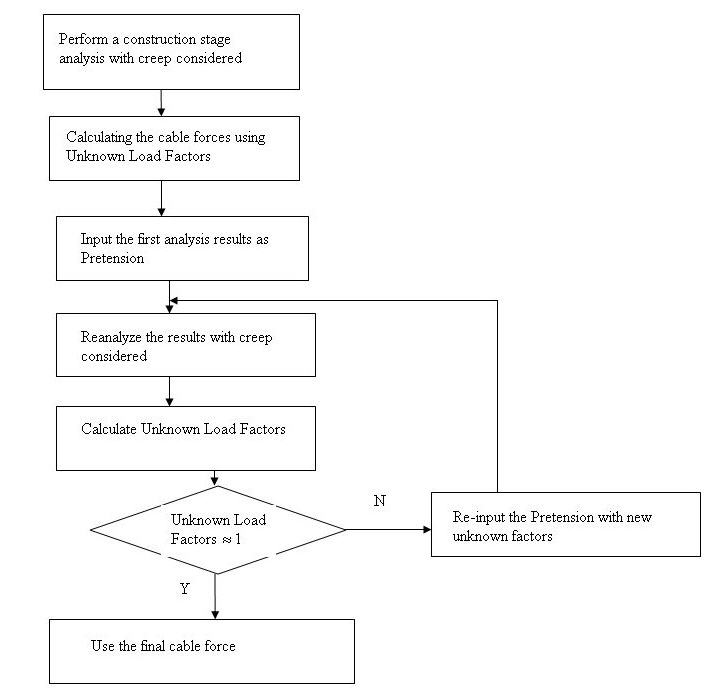
The flow chart to analyze cable forces for each construction stage
When using this function to perform automatic iterative analysis the following should be known. Whenever a new Pretension of the cables are inputted a new model file (mgb file) will be produced, and the program will provide as many analysis as the number of iterate the program is requested. The analysis may stop when the Unload Load Factor reaches 1. Then all the cable forces inputted to the final model file will be the optimized cable force during construction.
|
|
|
 : Load combinations ard automatically
generated by using the calculated Unknown Load Factors.
: Load combinations ard automatically
generated by using the calculated Unknown Load Factors.