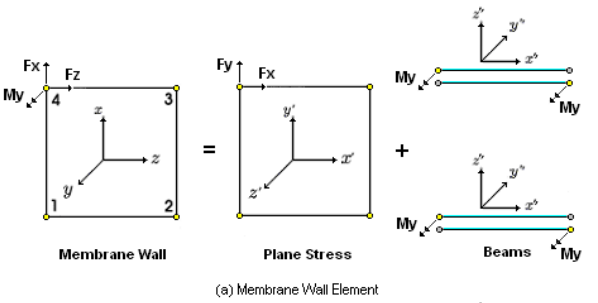
Create Elements
Create elements.
From the Main Menu select Node/Element > Elements > Create Elements.
Shortcut key: [Alt]+1
Click
|
 Material
Material
Select a material property number, or select a material property name provided that the material property data have been already defined.
No.: Type in a number on the keyboard or use the mouse to enter the number.
Name: Select a material property name.
Click ![]() to add, inquire, modify or delete material property data. Material
properties can be entered either before or after creating elements.
to add, inquire, modify or delete material property data. Material
properties can be entered either before or after creating elements.
 Section (or Thickness)
Section (or Thickness)
Select a section (thickness) number, or select a section(thickness) name provided that the section (thickness) data have been already defined.
No.: Type in a number on the keyboard or use the mouse to enter the number.
Name: Select a section (thickness) name.
Click ![]() to add, inquire, modify or delete section (thickness) data. Section
data can be entered either before or after creating elements.
to add, inquire, modify or delete section (thickness) data. Section
data can be entered either before or after creating elements.
 Orientation
Orientation
When elements are of a line type (Truss, Beam, etc.), Beta Angle or the coordinates of Reference Point are specified to define the orientation of sections.
If the coordinates of the Reference Point are entered, MIDAS/Gen internally computes the angle of the point and enters the angle as a Beta Angle automatically.
If the coordinates of the Reference Vector are entered, z-axis of an element is placed on the plane containing the Vector.
midas Gen uses the Beta Angle (β) conventions to identify the orientation of each cross-section. The Beta Angle relates the ECS to the GCS. The ECS x-axis starts from node N1 and passes through node N2 for all line elements. The ECS z-axis is defined to be parallel with the direction of "l" dimension of cross-sections. That is, the y-axis is in the strong axis direction. The use of the right-hand rule prevails in the process.
If the ECS x-axis for a line element is parallel with the GCS Z-axis, the Beta angle is defined as the angle formed from the GCS X-axis to the ECS z-axis. The ECS x-axis becomes the axis of rotation for determining the angle using the right-hand rule. If the ECS x-axis is not parallel with the GCS Z-axis, the Beta angle is defined as the right angle to the ECS x-z plane from the GCS Z-axis (See below).

(a) Case of vertical members (ECS x-axis is parallel with the global Z-axis)
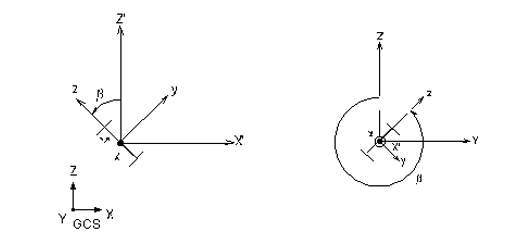
(b) Case of horizontal or diagonal members (ECS x-axis is not parallel with the global Z-axis.)
Beta Angle Conventions

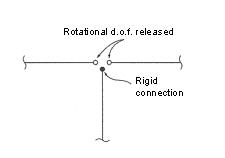
 Nodal Connectivity
Nodal Connectivity
Enter the node numbers defining the element in accordance with the (N1, N2,...) sequence shown in the figure that appears upon selecting Element Type.
Use the following two methods to enter the element's nodal connectivity.
Type in the node numbers in the Nodal Connectivity field.
Click the Nodal Connectivity field, which will turn the background color to pale green. Then, assign consecutively the desired node points in the Model Window to enter elements. If there is no node at the assigned point, a new node is created. It is quite convenient to create elements when Point Grid (or Line Grid) , Grid Snap, Node Snap and Elements Snap. are activated.
If Ortho option is selected the mouse cursor snaps to the entities only in the directions parallel to the currently active coordinate axes (UCS or GCS) from the first point selected.
The nodal locations defining the new elements are entered by directional axes, relative distances or element lengths/angles.
x,y,z:
The coordinates of the connecting point of an element are entered
in the data entry field, then press the enter key on the keyboard
or click ![]() .
.
dx,
dy, dz: Enter a distance relative to the reference point
and press the enter key on the keyboard or click ![]() , If characters
are included in the string of numerical values, MIDAS/Gen recognizes
them as a relative distance, irrespective of which one of the
three methods of data entry is selected
, If characters
are included in the string of numerical values, MIDAS/Gen recognizes
them as a relative distance, irrespective of which one of the
three methods of data entry is selected
Example: '0,20,10' of ' dx, dy, dz' are expressed as '@10, 20, 10' .
l,
theta: l represents the length of an element. Theta represents
the angle by which the element direction is rotated with respect
to x-axis of the current coordinate system. Once the data are
entered, press the enter key on the keyboard or click ![]() .
.
If characters, '@' and/or '<' are included in the string of numerical values, MIDAS/Gen recognizes the numbers as l and theta, irrespective of which one of the three methods of data entry is selected.
Example: '10, 15' of 'l, theta' are expressed as '@10<15'
Note
The origin of the current coordinate system is assigned as the
reference point initially. Subsequently, the last point used becomes
the reference point. To confirm the location of the reference
point, enter '@0' in the data field and press the Enter key on
the keyboard.
 Intersect
Intersect
If Intersect Node is selected and existing nodes are on the element, the element is divided at the existing nodal positions irrespective of the element type.
If Intersect Element is selected and the line element created intersects with an existing line elements, nodes are automatically created and the line elements are divided at the intersections.
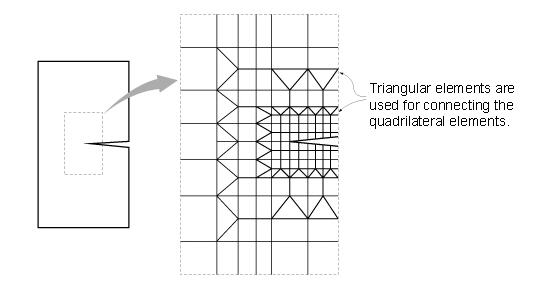
If Create Intersecting Nodes is selected and even if there are no interior nodes in the created plate and solid elements, nodes are created at the intersections of the lines extended by the exterior nodes and plate or solid elements are subsequently created.
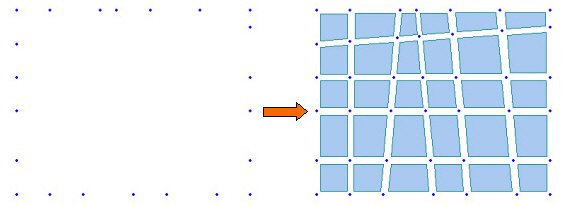
Example of Create Intersecting Nodes application
![]() Revision of Gen 2015 (v1.1)
Revision of Gen 2015 (v1.1)