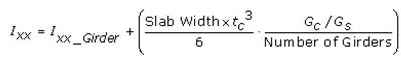Section
Enter section properties for line elements (Truss, Tension-only, Compression-only, Cable, Gap, Hook, Beam Element).
From the Main Menu select Properties > Section > Section Properties.
-
To enter new or additional section properties
Click ![]() in the Properties dialog box and enter the following: Enter the section properties by entry types.
in the Properties dialog box and enter the following: Enter the section properties by entry types.
-
Modification of previously entered section data
Select the section to be modified from the list in the Section dialog box and click ![]() to modify the related data.
to modify the related data.
-
Removal of previously entered section data
Select the section to be deleted from the list in the Section dialog box and click ![]() .
.
-
To copy previously entered section data
Select the section to be copied from the list in the Section dialog box and click ![]() .
.
-
To modify section data from an existing fn.MCB file
Click ![]() and select the MCB file containing the section data or specify a file name then click
and select the MCB file containing the section data or specify a file name then click ![]() . [Details]
. [Details]
Section List
Display section data contained in the existing fn.MCB file.
Selected List
Select section data to be imported and register them in the Selected List.
Note
If a fn.MCB is selected, all the section data contained in the existing fn.MCB file are registered in the Selected List.
Numbering Type
Specify the Import mode for section numbers.
Keep ID
Import the data keeping the same section numbers.
New ID
Assign new numbers to the imported section data.
-
To modify previously entered section property numbers
Select the section property numbers to be renumbered from the list in the Properties dialog box and modify the related data followed by clicking ![]() . [Details]
. [Details]
Start number
Assign a new starting number for the material to be modified.
Increment
Enter the increment for numbering material property numbers.
Change element's material number
Modify a material property number. Using this option will modify the previously defined material property number. If this option is not checked, the selected material having previously defined number will become undefined and the additional user-defined material number will be created without any assigned elements.
 Section ID
Section ID
Section number (Auto-set to the last section number +1)
Note
Up to 999999 Section ID's can be assigned.
 Name
Name
Section name (Sect. Name by default if not specified)
 Offset
Offset
Display the section Offset currently set. Location of the Centroid of a section is set as default. Click ![]() to specify a section Offset away from the Centroid. Use
to specify a section Offset away from the Centroid. Use ![]() Hidden to verify the input.
Hidden to verify the input.
Offset: Specify the section Offset from the location options shown in the figure below.
Horizontal Offset: Specify the Offset in the transverse direction. "to Extreme Fiber" assigns the offset to the outer-most point. For a specific location of Offset, select 'User"and enter the distance from the "Centroid" to the desired Offset location. Unless the Offset is "Center-Center" the Horizontal Offset can be entered as the "User" type. For a tapered (non-prismatic) section, data input for the J-end also becomes activated.
Vertical Offset: Specify the Offset in the vertical direction. "to Extreme Fiber" assigns the offset to the outer-most point. For a specific location of Offset, select "User" and enter the distance from "Centroid" to the desired Offset location. Unless the Offset is "Center-Center" the Vertical Offset can be entered as the "User" type. For a tapered (non-prismatic) section, data input for the J-end also becomes activated.
Note 1
When Offset distance is specified, a positive (+) sign applies to Center-to-outward for Centroid reference and Extreme-to-inward for Extreme Fiber reference.
User Offset Reference: When section offset distance is specified as the "User" type, define the reference location.
Centroid: Specify the offset distance relative to the centroid of the section.
Extreme Fiber(s): Specify the offset distance relative to Left/Right & Top/Bottom.
Note 2
When User type is specified, the Offset distance and direction are entered relative to Centroid irrespective of the Center option (Centroid or Center of Section). For example, specifying "Offset: Left-Center", "Center Loc.: Center of Section" and "Horizontal offset: 0.5 " User type" will result in an Offset 0.5" to the left of the Centroid. And if the Offset option is "Left-Center" and the Center option is Center of Section the User type for Horizontal offset becomes activated and the User type for Vertical offset becomes inactivated. The Horizontal offset defined as User type here becomes the Centroid, and the Vertical offset fixed to Center becomes the "Center of Section"
Note 3
When FCM Wizard is used, and "Apply the Centroid of Pier Table Section Option" is selected, the node locations of the girder will be changed as follows:
Offset: Center-Top
User Offset Reference: Extreme Fiber(s)
Vertical Offset: User, Offset Distance (i & j) = Pier Table section height-Centroid of Pier Table section
Note 4 Usage tip of Section Offset
-
-
-
Internal process of section offset
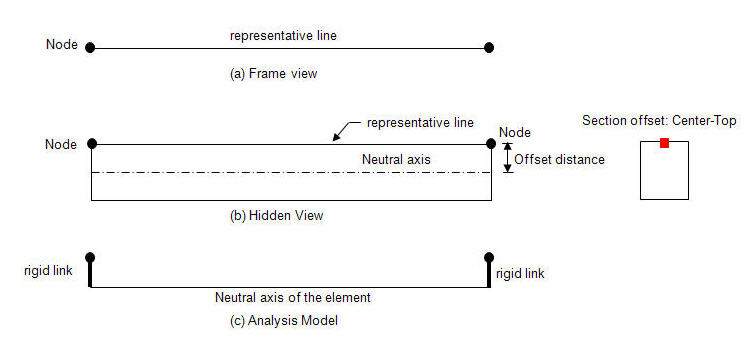
A beam element is defined by two nodes and a line connecting the two nodes. This line becomes a reference line representing the beam element, which usually coincides with the neutral axis of the beam element. If a section offset is assigned to a section, the neutral axis of the member shifts by the specified offset distance, and the element reference line is placed at the offset location. The reference line is used for selecting the element, assigning loads, displaying member forces, etc. The offset of the neutral axis of the member relative to the reference line in turn is reflected in analysis as shown in the figure (c) below.
-
1. Nodal Load
When an offset is assigned to a section, a nodal load remains applied to the corresponding node regardless of the offset. This results in moments due to the offset to the neutral axis as shown in the case of figure b.
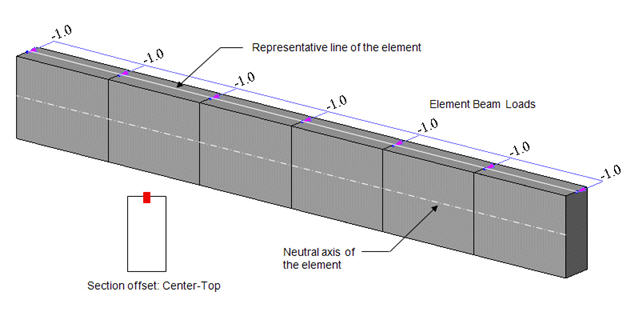
2. Element Beam Loads
Element beam load is applied to the neutral axis of the element regardless of the section offset position. In the diagram below, the element beam load is applied to the neutral axis even though the section is offset from the reference line. Therefore torsional moment from the element beam load is not induced by the offset. Note however that the element beam load is displayed on the reference line as if it is applied to the reference line, but it is actually applied to the neutral axis.
-
Calculation of member forces of the elements for which section offset is applied
Member forces (axial force, shear force, moment & torsion) of a beam element are calculated relative to the neutral axis. This is true even when a section offset is applied. However, the member force diagrams are displayed on the reference line. This does not mean the member forces are calculated relative to the reference line.
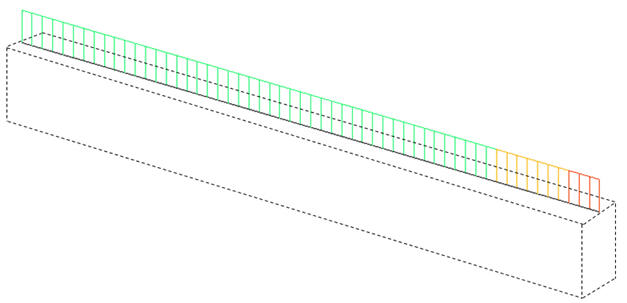
Member forces diagram when section offset is applied
-
Comparison between section offset and beam end offset
An offset of a section can be defined using the Beam End Offset function. For a prismatic section, a Section offset is assigned to both
i-end and j-end identically. However, Beam End Offset can assign different offsets at i-end and j-end independently. Section offset is more useful for a tapered section as opposed to Beam End Offset as shown in the figure below.
In addition, Section offset and Beam End Offset cannot be assigned simultaneously. In such a case, Section offset is ignored, and Beam End Offset only becomes effective.
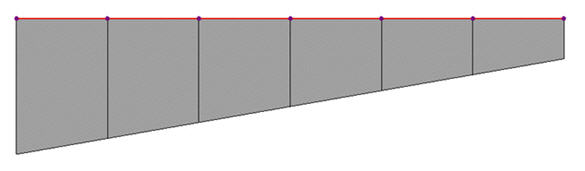
Modeling of a tapered section group when a Section offset (Center-Top) is defined
-
-
![]() : Display the Offset specified from the Change Offset dialog box in the guide diagram of Section Data window.
: Display the Offset specified from the Change Offset dialog box in the guide diagram of Section Data window.
 Consider Shear Deformation
Consider Shear Deformation
Select whether to consider shear deformation. This option will be applicable for structural analysis, but will not affect the effective shear areas that appear by clicking ![]() .
.
 Consider Warping Effect (7th DOF)
Consider Warping Effect (7th DOF)
Select whether to consider warping effect. In case of non-uniform torsion which occurs when warping deformation is constrained, torque is resisted by St.Venant torsional shear stress & warping torsion. The effects of warping torsion can be simulated in 1D beam elements for more accurate results in case of the curved member, eccentric loading, and difference in centroid and shear center.
When “Consider Warping Effect(7th DOF)” is considered, warping constant (Iw), warping function (w1, w2, w3, w4), and shear strain due to twisting moment (γxy1, γxy2, γxy3, γxy4, γxz1, γxz2, γxz3, γxz4) can be checked in Section Properties dialog box.
Note. Applicable element types, boundary conditions and analysis type
Applicable element type: General beam/Tapered beam
Applicable boundary condition: Supports, Beam End Release
Applicable analysis type : Linear Static , Eigenvalue , Response Spectrum, Construction Stage Analysis
Related post-processing: Reactions, Displacements, Beam Forces/Moments, Beam Stresses
 Section Properties
Section Properties
Click ![]() to display the section property data. The section property data table is either calculated from the main dimensions or obtained from the DB depending on the method of data entry. [Details]
to display the section property data. The section property data table is either calculated from the main dimensions or obtained from the DB depending on the method of data entry. [Details]
Area: Cross sectional area
Asy: Effective Shear Area for shear force in the element's local y-direction
It becomes inactive when Shear Deformation is not considered.
Asz: Effective Shear Area for shear force in the element's local z-direction
It becomes inactive when Shear Deformation is not considered.
Ixx: Torsional Resistance about the element's local x-axis
Iyy: Moment of Inertia about the element's local y-direction
Izz: Moment of Inertia about the element's local z-direction
Cyp: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the extreme fiber of the element in the local (+)y-direction
Cym: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the extreme fiber of the element in the local (-)y-direction
Czp: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the extreme fiber of the element in the local (+)z-direction
Czm: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the extreme fiber of the element in the local (-)z-direction
Qyb: Shear Coefficient for the shear force applied in the element's local z-direction
Qzb: Shear Coefficient for the shear force applied in the element's local y-direction
Peri: O: Total perimeter of the section
Peri: I: Inside perimeter length of a hollow section
y1, z1: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the Location 1 (used for computing combined stress)
y2, z2: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the Location 2 (used for computing combined stress)
y3, z3: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the Location 3 (used for computing combined stress)
y4, z4: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the Location 4 (used for computing combined stress)
Zyy: Plastic Section Modulus about the element local y-direction
Zzz: Plastic Section Modulus about the element local z-direction
Note 1
All the above section property data except for Area and Peri are required for beam elements.
Note 2
The shear deformations are neglected if the effective shear areas are not specified. Cyp, Cym, Czp and Czm are used to calculate the bending stresses. Qyb and Qzb are used to calculate the shear stresses. Peri is used to calculate the Painting Area.
Note 3
Zyy and Zzz are used to calculate the strength for pushover analysis when Value Type Steel Section has been assigned Design > Pushover Analysis > Define Hinge Properties.
Note 4 Element Stiffness data
Sections can be defined by the stiffness data entries even if the section dimensions (H, B1, ... , etc.) are not entered.
-
The cross-sectional area of a member is used to compute axial stiffness and stress when the member is subjected to a compression or tension force. Figure 1 illustrates the calculation procedure.
Cross-sectional areas could be reduced due to member openings and bolt or rivet holes for connections. midas does not consider such reductions. Therefore, if necessary, the user is required to modify the values using the option 2 above and his/her judgment.
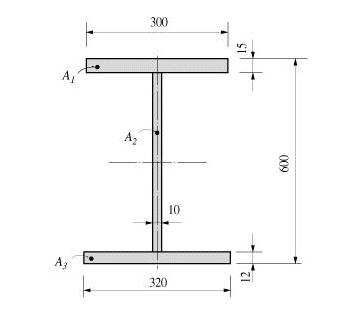
Area = +dA = A1 + A2 + A3
= (300 x 15) + (573 x 10) + (320 x 12)
= 14070
<Figure 1> Example of cross-sectional area calculation
-
Effective Shear Areas (Asy, Asz)
The effective shear areas of a member are used to formulate the shear stiffness in the y- and z-axis directions of the cross-section.
If the effective shear areas are omitted, the shear deformations in the corresponding directions are neglected.
When midas computes the section properties by the option 1 or 3, the corresponding shear stiffness components are automatically calculated. Figure 2 outlines the calculation methods.
Asy: Effective shear area in the ECS y-axis direction
Asz: Effective shear area in the ECS z-axis direction
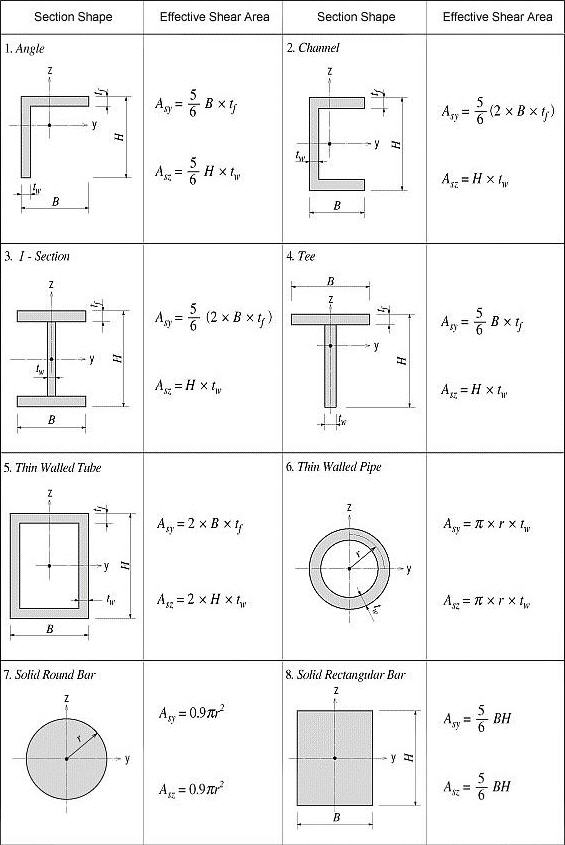
<Figure 2> Effective Shear Area calculations
-
Torsional resistance refers to the stiffness resisting torsional moments. It is expressed as
<Eq. 1>
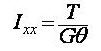
where,
Ixx: Torsional Constant
T: Torsional moment or torque
G: Shear Modulus of Elasticity
θ : Angle of twist
The torsional stiffness expressed in Eq. 1 must not be confused with the polar moment of inertia that determines the torsional shear stresses. However, they are identical to one another in the cases of circular or thick cylindrical sections.
No general equation exists to satisfactorily calculate the torsional resistance applicable for all section types. The calculation methods widely vary for open and closed sections and thin and thick thickness sections.
For calculating the torsional resistance of an open section, an approximate method is used; the section is divided into several rectangular sub-sections and then their resistances are summed into a total resistance, Ixx, calculated by the equation below.
<Eq. 2>
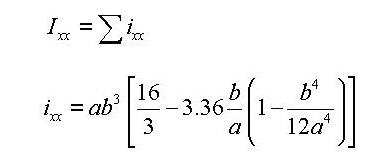
for a e b
where,
Ixx: Torsional resistance of a (rectangular) sub-section
2a: Length of the longer side of a sub-section
2b: Length of the shorter side of a sub-section
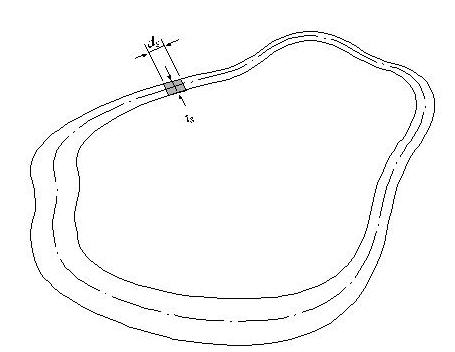
Figure 3 illustrates the equation for calculating the torsional resistance of a thin walled, tube-shaped, closed section.
<Eq. 3>
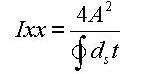
where,
A: Area enclosed by the mid-line of the tube
ds: Infinitesimal length of thickness centerline at a given point
t: Thickness of tube at a given point
For those sections such as bridge box girders, which retain the form of thick walled tubes, the torsional stiffness can be obtained by combining the above two equations, Eq. 1 and Eq. 3.
Torsional resistance:
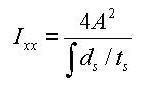
Shear stress at a given point:
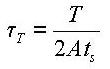
Thickness of tube at a given point:
<Figure 3> Torsional resistance of a thin walled, tube-shaped, closed section
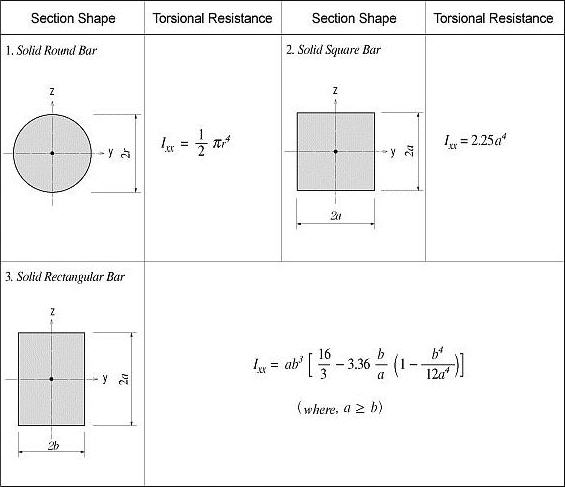
<Figure 4> Torsional resistance of solid sections
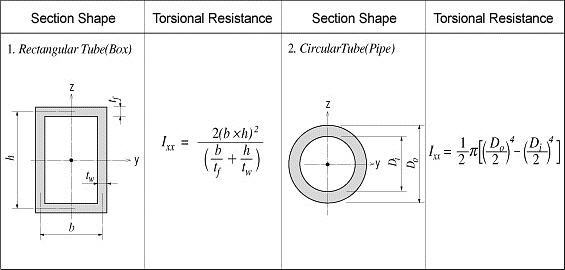
<Figure 5> Torsional resistance of thin walled, closed sections
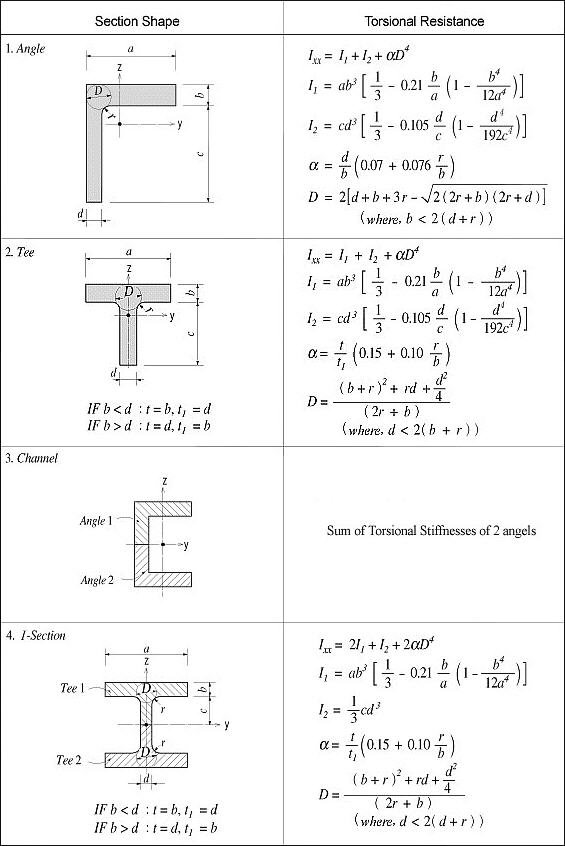
<Figure 6> Torsional resistance of thick walled, open sections
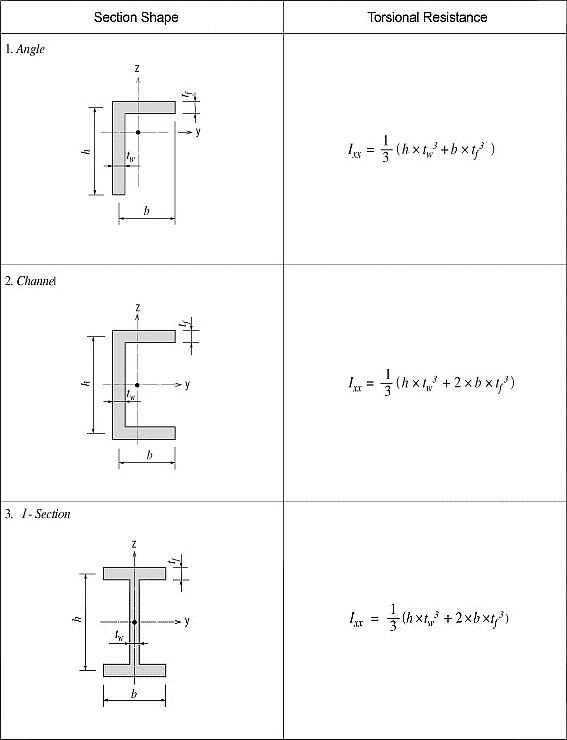
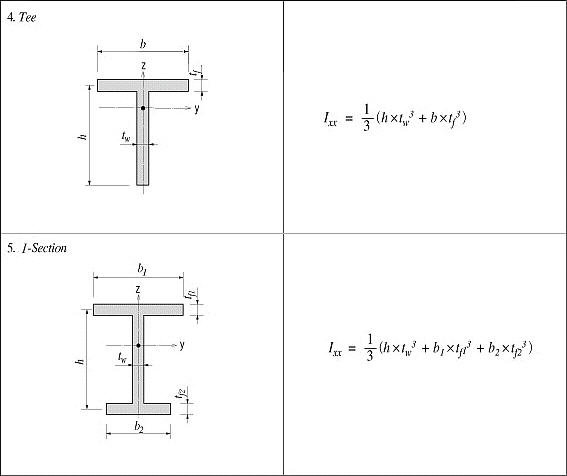
<Figure 7> Torsional resistance of thin walled, open sections
In practice, combined sections often exist. A combined built-up section may include both closed and open sections. In such a case, the stiffness calculation is performed for each part, and their torsional stiffnesses are summed to establish the total stiffness for the built-up section.
For example, a double I-section shown in Figure 8(a) consists of a closed section in the middle and two open sections, one on each side.
-
The torsional resistance of the closed section (hatched part)
<Eq. 4>
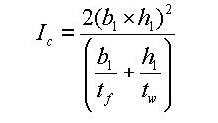
-
The torsional resistance of the open sections (unhatched parts)
<Eq. 5>
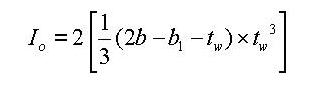
-
The total resistance of the built-up section
<Eq. 6>
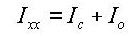
Figure 8(b) shows a built-up section made up of an I-shaped section reinforced with two web plates, forming two closed sections. In this case, the torsional resistance for the section is computed as follows:
If the torsional resistance contributed by the flange tips is negligible relative to the total section, the torsional property may be calculated solely on the basis of the outer closed section (hatched section) as expressed in Eq. 7.
<Eq. 7>
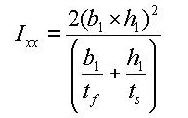
If the torsional resistance of the open sections is too large to ignore, then it should be included in the total resistance.
(a) Section consisted of closed and open sections
(b) Section consisted of two closed sections
<Figure 8> Torsional resistance of built-up sections
-
Area Moment of Inertia (Iyy, Izz)
The area moment of inertia is used to compute the flexural stiffness resisting bending moments. It is calculated relative to the centroid of the section.
-
Area moment of inertia about the ECS y-axis
<Eq. 8>
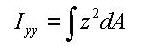
-Area moment of inertia about the ECS z-axis
<Eq. 9>
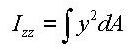
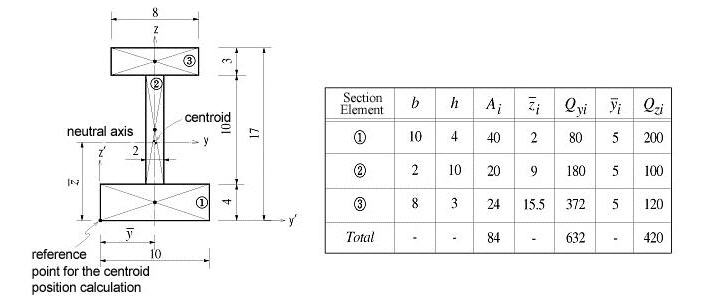
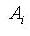 : area
: area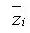 : distance from the reference point to the centroid of the section element in the z-axis direction
: distance from the reference point to the centroid of the section element in the z-axis direction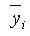 : distance from the reference point to the centroid of the section element in the y-axis direction
: distance from the reference point to the centroid of the section element in the y-axis direction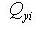 : first moment of area relative to the reference point in the y-axis direction
: first moment of area relative to the reference point in the y-axis direction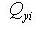 : first moment of area relative to the reference point in the z-axis direction
: first moment of area relative to the reference point in the z-axis direction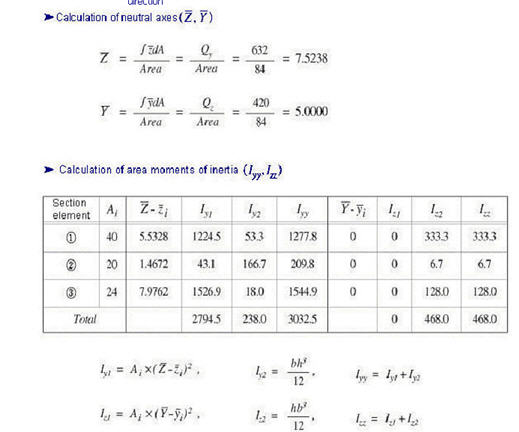
<Figure 9> Example of calculating area moments of inertia
-
Area Product Moment of Inertia (Iyz)
The area product moment of inertia is used to compute stresses for non-symmetrical sections, which is defined as follows:
<Eq. 10>
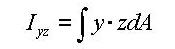
Sections that have at least one axis of symmetry produce Iyz=0. Typical symmetrical sections include I, pipe, box, channel and tee shapes, which are symmetrical about at least one of their local axes, y and z. However, for non-symmetrical sections such as angle shaped sections, where Iyz`0, the area product moment of inertia should be considered for obtaining stress components.
The area product moment of inertia for an angle is calculated as shown in Figure 10.
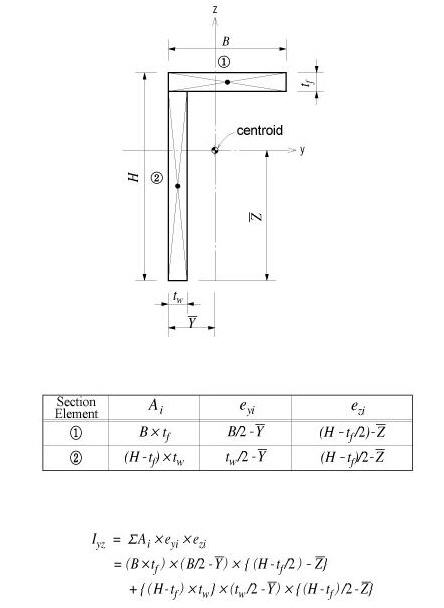
<Figure 10> Area product moment of inertia for an angle
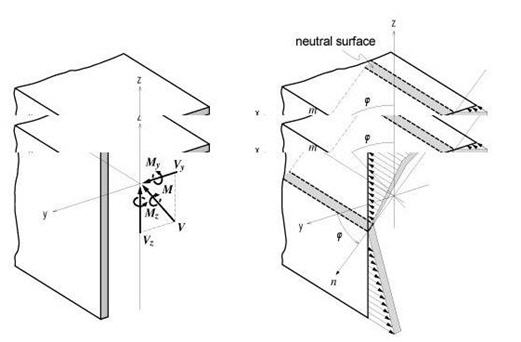
<Figure 11> Bending stress distribution of a non-symmetrical section
The neutral axis represents an axis along which bending stress is 0 (zero). As illustrated in the right-hand side of Figure 11, the n-axis represents the neutral axis, to which the m-axis is perpendicular. Since the bending stress is zero at the neutral axis, the direction of the neutral axis can be obtained from the relation defined as
<Eq. 11>
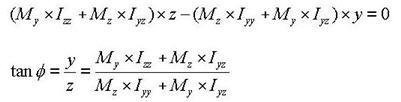
The following represents a general equation applied to calculate the bending stress of a section:
<Eq. 12>
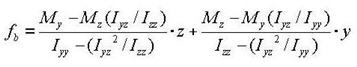
In the case of an I shaped section, Iyz=0, hence the equation can be simplified as:
<Eq. 13>
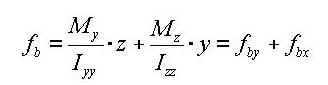
where,
Iyy: Area moment of inertia about the ECS y-axis
Izz: Area moment of inertia about the ECS z-axis
Iyz: Area product moment of inertia
y: Distance from the neutral axis to the location of bending stress calculation in the ECS y-axis direction
z: Distance from the neutral axis to the location of bending stress calculation in the ECS z-axis direction
My: Bending moment about the ECS y-axis
Mz: Bending moment about the ECS z-axis
The general expressions for calculating shear stresses in the ECS y and z-axes are:
<Eq. 14>
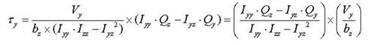
<Eq. 15>
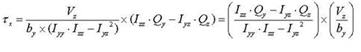
where,
Vy: Shear force in the ECS y-axis direction
Vz: Shear force in the ECS z-axis direction
Qy: First moment of area about the ECS y-axis
Qz: First moment of area about the ECS z-axis
by: Thickness of the section at which a shear stress is calculated, in the direction normal to the ECS z-
axis
bz: Thickness of the section at which a shear stress is calculated, in the direction normal to the ECS y-axis
-
The first moment of area is used to compute the shear stress at a particular point on a section. It is defined as follows:
<Eq. 16>
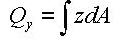
<Eq. 17>
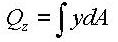
When a section is symmetrical about at least one of the y and z-axis, the shear stresses at a particular point are:
<Eq. 18>
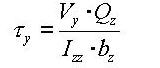
<Eq. 19>
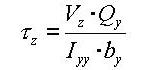
where,
Vy: Shear force acting in the ECS y-axis direction
Vz: Shear force acting in the ECS z-axis direction
Iyy: Area moment of inertia about the ECS y-axis
Izz: Area moment of inertia about the ECS z-axis
by: Thickness of the section at the point of shear stress calculation in the ECS y-axis direction
bz: Thickness of the section at the point of shear stress calculation in the ECS z-axis direction
-
Shear Factor for Shear Stress (Qyb, Qzb)
The shear factor is used to compute the shear stress at a particular point on a section, which is obtained by dividing the first moment of area by the thickness of the section.
<Eq. 20>
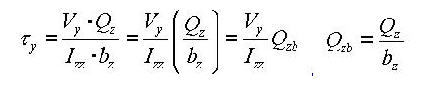
<Eq. 21>
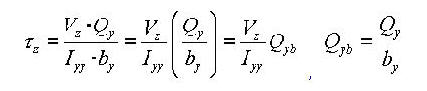
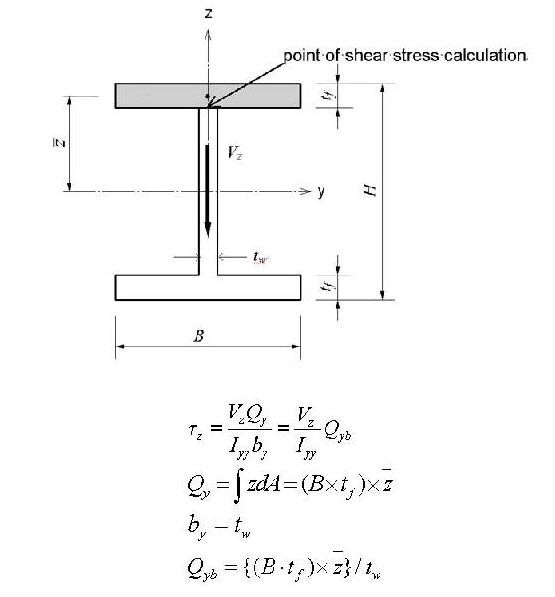
<Figure 12> Example of calculating a shear factor
-
Stiffness of Composite Sections
midas calculates the stiffness for a full composite action of structural steel and reinforced concrete. Reinforcing bars are presumed to be included in the concrete section. The composite action is transformed into equivalent section properties.
The program uses the elastic moduli of the steel (Es) and concrete (Ec) defined in the SSRC79 (Structural Stability Research Council, 1979, USA) for calculating the equivalent section properties. In addition, the Ec value is decreased by 20% in accordance with the EUROCODE 4.
- Equivalent cross-sectional area
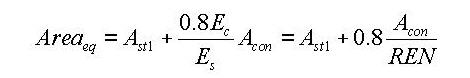
- Equivalent effective shear area
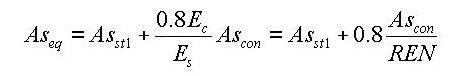
- Equivalent area moment of inertia
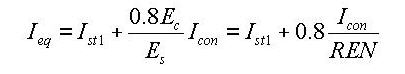
where,
Ast1: Area of structural steel
Acon: Area of concrete
Asst1: Effective shear area of structural steel
Ascon: Effective shear area of concrete
Ist1: Area moment of inertia of structural steel
Icon: Area moment of inertia of concrete
REN: Modular ratio (elasticity modular ratio of the structural steel to the concrete, Es/Ec)
- Equivalent torsional coefficient
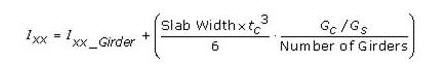
Note 5
Determining the positions of y1~4, z1~4 of a section imported from SPC [Details]
1. Divide the section into four quadrants.
2. Assign the positions furthermost from the centroid in each quadrant for checking stresses.
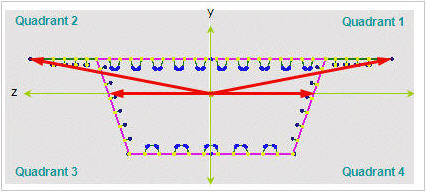
If the webs of a section are extensively sloped as in the above diagram, the points furthermost from the centroid may not be the lowest points of the section. Use caution that the stress checking positions of quadrants 3 & 4 may be selected differently from the expectation.
 Section Type
Section Type
-
[DB/User tab]
The section data can be entered by the following 2 methods in the dialog box:
1. Select a section from the DB (database) of the standard sections for a country.
2. Enter the main dimensions of a standardized section shape.
Section Shape List: Select a section shape (Angle, Channel, H-Section, T-Section, Box, Pipe, Double Angle, Star-battened Angle, Double Channel, Solid Rectangle, Solid Round, Octagon, Solid Octagon, R-Octagon, Track, Solid Track, Half Track, Cold Formed Channel, U-Rib & Inverted T-section).
User: Enter the main dimensions of a standardized section shape.
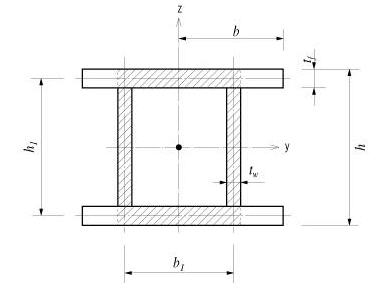
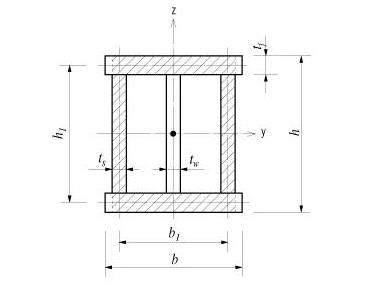
H, B1, ...: Refer to the dimension information diagram in the dialog box.
DB: Select a section from the DB of the standard sections for a country.
AISC2K(US): American Institute of Steel Construction, 2000 US Unit : lb, in
AISC2K(SI): American Institute of Steel Construction, 2000 SI Unit : kN, m, mm
AISC: American Institute of Steel Construction
CISC02(US): Canadian Institute of Steel Construction (US Unit : lb, in)
CISC02(SI): Canadian Institute of Steel Construction (SI Unit : kN, m, mm)
BS(S): British Standard
Note
BS indicates BS4-1 revised prior to 1993.
BS4 - 93: British Standard / BS 4-1 : 1993
DIN: Deutches Institut fur Normung e.v
UNI: Italian National Standard
GOST: Russian National Standard
STO_ASChM: Russian National Standard
JIS2K : Japanese Industrial Standards 2000
JIS: Japanese Industrial Standards
KS: Korean Industrial Standards
GB-YB05: Guojia Biao Zhun-Yejin Bu Biao Zhun
Pacific(SI): Bentley Pacific Standards (SI Unit : kN, m, mm)
IS84: Indian Standards
GB-YB05: Guojia Biao Zhun-Yejin Bu Biao Zhun(2005)
CNS91: Taiwan Standards
Sect. Name: Enter directly a DB section name or select a desired DB from the Section list. When the section name is directly entered, it must correspond to the format of the DB section names.
Ex) AISC: W36x280, BS: UB 406x178x54, DIN: HD400x288
Note
When specifying Double Angle or Double Channel sections, assign the sectional shape in the list and select User. Then, select DB and Sect. Name from Get Data from Single Angle (or Channel) or directly enter the main dimensions of the section.
-
[Value tab]
The section data can be entered by the following 3 methods in the dialog box:
1. Select a section from the DB (database) of the standard sections for a country.
2. Enter the main dimensions of a standardized section shape.
3. Import a section generated from SPC module.
Section Shape List: Assign a section shape to use.
Built-Up Section: Fabricated section
Note
Check in the case of a built-up section and leave it blank in the case of a rolled steel section. The data is referred to for strength verification for steel members and compiling material quantities in BOM.Size
H, B1, ...: Refer to the diagram denoting section dimensions in the dialog box.
The structure can be analyzed only with the stiffness data even if the section dimensions are not specified.
Section Properties
The main section dimensions entered in Size are used to calculate and display the section stiffness.
Area: Cross sectional area
Asy: Effective Shear Area for shear force in the element's local y-direction
It becomes inactive when Shear Deformation is not considered.
Asz: Effective Shear Area for shear force in the element's local z-direction
It becomes inactive when Shear Deformation is not considered.
Ixx: Torsional Resistance about the element's local x-axis
Iyy: Moment of Inertia about the element's local y-direction
Izz: Moment of Inertia about the element's local z-direction
Cyp: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the extreme fiber of the element in the local (+)y-direction
Cym: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the extreme fiber of the element in the local (-)y-direction
Czp: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the extreme fiber of the element in the local (+)z-direction
Czm: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the extreme fiber of the element in the local (-)z-direction
Qyb: Shear Coefficient for the shear force applied in the element's local z-direction
Qzb: Shear Coefficient for the shear force applied in the element's local y-direction
Peri:O: Total perimeter of the section
Peri:I: Inside perimeter length of a hollow section
Note
The value of Peri:I is '0' for an I-shaped section since the section is not hollow.Cent:y: Centroidal distance in ECS y-axis
Cent:z: Centroidal distance in ECS z-axis
y1, z1: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the Location 1 (used for computing combined stress) The user may specify
the location of the stress display.
y2, z2: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the Location 2 (used for computing combined stress) The user may specify
the location of the stress display.
y3, z3: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the Location 3 (used for computing combined stress) The user may specify
the location of the stress display.
y4, z4: Distance from the section's neutral axis to the Location 4 (used for computing combined stress) The user may specify
the location of the stress display.
Zyy: Plastic Section Modulus about the element local y-direction
Zzz: Plastic Section Modulus about the element local z-direction
-
[SRC tab]
Enter the section property data for steel RC composite members in the dialog box.
Shape: Assign a section shape to use.
Note
New Cross I Section and Combined T-Section were incorporated.
Concrete Data: Enter the outer dimensions of the RC section of a steel-encased concrete section.
Steel Data: Enter the steel section data.
User: Enter the main dimensions of a standardized section shape.
H, B1, ...: Refer to the dimension information diagram in the dialog box.
DB: Select a section from the DB of the standard sections for a country.
AISC2K(US): American Institute of Steel Construction, 2000 US Unit : lb, in
AISC2K(SI): American Institute of Steel Construction, 2000 SI Unit : kN, m, mm
AISC: American Institute of Steel Construction
CISC02(US): Canadian Institute of Steel Construction (US Unit : lb, in)
CISC02(SI): Canadian Institute of Steel Construction (SI Unit : kN, m, mm)
BS(S): British Standard
Note
BS indicates BS4-1 revised prior to 1993.
BS4 - 93: British Standard / BS 4-1 : 1993
DIN(S): Deutches Institut fur Normung e.v
JIS2K : Japanese Industrial Standards 2000
JIS: Japanese Industrial Standards
KS: Korean Industrial Standards
GB-YB: Guojia Biao Zhun-Yejin Bu Biao Zhun
Pacific(SI): Bentley Pacific Standards (SI Unit : kN, m, mm)
IS84: Indian Standards
CNS91: Taiwan Standards
Steel Name: Enter directly a DB section name or select a desired DB from the Section list. When the section name is directly entered, it must correspond to the format of the DB section names.
Ex) AISC: W36x280, BS: UB 406x178x54, DIN: HD400x288, JIS, KS: H 400x200x8/13
Material: Enter material properties for steel and concrete constituting steel RC composite sections.
Click
 to select the material properties for steel and concrete stored in the DB for a country. The following items are automatically entered:
to select the material properties for steel and concrete stored in the DB for a country. The following items are automatically entered:Es/Ec: Modulus of Elasticity Ratio of steel relative to concrete
Ds/Dc: Specific Weight (Density) Ratio of steel relative to concrete
Ps: Poisson's Ratio for steel
Pc: Poisson's Ratio for concrete
Combined Ratio of Conv.: Stiffness Reduction Factor of concrete [Default = 1.0]
Note
When RC is converted into steel for calculating the SRC section stiffness, Conv. Stiffness Factor is applied to reduce the stiffness of RC.Replace: Assign Steel to be the reference when calculating stiffness of a composite section
Note
MIDAS/Civil converts RC into equivalent steel for SRC section stiffness calculation.
-
[Combined tab]
In this dialog box, enter the section properties for a combined section made up by two standard section types.
User: Enter the main dimensions of standardized section shapes.
DB: Select the sections from the DB of the standard sections for a country.
AISC2K(US): American Institute of Steel Construction, 2000 US Unit : lb, in
AISC2K(SI): American Institute of Steel Construction, 2000 SI Unit : kN, m, mm
AISC: American Institute of Steel Construction
CISC02(US): Canadian Institute of Steel Construction (US Unit : lb, in)
CISC02(SI): Canadian Institute of Steel Construction (SI Unit : kN, m, mm)
BS(S): British Standard
Note
BS indicates BS4-1 revised prior to 1993.
BS4 - 93: British Standard / BS 4-1 : 1993
DIN(S): Deutches Institut fur Normung e.v
JIS2K : Japanese Industrial Standards 2000
JIS: Japanese Industrial Standards
KS: Korean Industrial Standards
GB-YB: Guojia Biao Zhun-Yejin Bu Biao Zhun
Pacific(SI): Bentley Pacific Standards (SI Unit : kN, m, mm)
IS84: Indian Standards
CNS91: Taiwan Standards
Data 1, Data 2: Enter the section data for individual components constituting the combined section.
Sect. Name: Enter directly a DB section name or select a desired DB from the Section list. When the section name is directly entered, it must correspond to the format of the DB section names.
Ex) AISC: W36x280, BS: UB 406x178x54, DIN: HD400x288, JIS, KS: H 400x200x8/13
H, B, ...: Refer to the diagram denoting section dimensions in the dialog box.
Note Applicable composite section DB for design
1. Design code : KSSC-ASD03, AISC-ASD89, TWN-ASD90
2. Section DB : H-T Combined Shape, 2T(Web Opened H), H-Shape with 2T or Web
-
[Tapered tab]
In this dialog box, enter the section properties for both ends of a line element to define a non-uniform section (Non-prismatic Section/ Tapered Section) of identical shape.(Refer to Note)
Section Shape List: Applicable tapered section shapes are shown below. For PSC, Composite Type or General Section of Value type, pre-defined sections can be brought in from the Section DB.
DB/User: All sections except for the R-Octagon section
Value: All sections except for the R-Octagon section

PSC: All PSC Type sections

Composite: Typical 4 composite sections (Steel-Box, Steel-I, PSC-I & PSC-T)

Value: Assign value when the user directly enters the section stiffness data.
Enter the section dimensions for section-i and j separately and click
 . Then, the user may modify the auto-calculated stiffness data or directly enter the stiffness data without entering the section dimensions.
. Then, the user may modify the auto-calculated stiffness data or directly enter the stiffness data without entering the section dimensions.User: Enter the main dimensions of standardized section shapes.
DB: Select the sections from the DB of the standard sections for a country.
AISC2K(US): American Institute of Steel Construction, 2000 US Unit : lb, in
AISC2K(SI): American Institute of Steel Construction, 2000 SI Unit : kN, m, mm
AISC: American Institute of Steel Construction
CISC02(US): Canadian Institute of Steel Construction (US Unit : lb, in)
CISC02(SI): Canadian Institute of Steel Construction (SI Unit : kN, m, mm)
BS(S): British Standard
DIN(S): Deutches Institut fur Normung e.v
JIS2K : Japanese Industrial Standards 2000
JIS: Japanese Industrial Standards
KS: Korean Industrial Standards
GB-YB: Guojia Biao Zhun-Yejin Bu Biao Zhun
Pacific(SI): Bentley Pacific Standards (SI Unit : kN, m, mm)
IS84: Indian Standards
CNS91: Taiwan Standards
Section-i, Section-j: Enter directly each section name corresponding to the starting section-i and the ending section-j or select the desired DB from the section list to describe the tapered section. When the section names are directly entered, they must correspond to the DB section name format.
Ex) AISC: W36x280, BS: UB 406x178x54, DIN: HD400x288, JIS, KS: H 400x200x8/13
y Axis Variation: Dimensional variation affects the moment of inertia about the element local y-axis along the length.
z Axis Variation: Dimensional variation affects the moment of inertia about the element local z-axis along the length.
Linear: linear variation along the element local x-direction
Parabolic: parabolic variation along the element local x-direction
Cubic: cubic variation along the element local x-direction
Note 1
Calculation of section properties as per Dimensional Variation [Details]
Once the main section dimensions of both ends of a tapered section member are entered, the section properties are considered to vary from the i end (element connection node N1) to the j end (element connection node N2) along the member length. The cross sectional areas, effective shear areas and torsional resistances are assumed to vary linearly from i to j along the element local x-axis. The moments of inertia are assumed to vary linearly, parabolically or cubically depending on the directions of section changes.
For instance, in the figures below, the variations of Iyy and Izz can be expressed as follows:
Moments of Inertia about strong and weak axes for a rectangular section <See figure below>
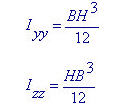
When the width (B) is constant and the height (H) varies, the moments of inertia show a cubic variation about the strong axis and a linear variation about the weak axis. Namely, Iyy Variation = 'Cubic', Izz Variation = 'Linear'.
Moments of Inertia about strong and weak axes for an I-section <See figure below>
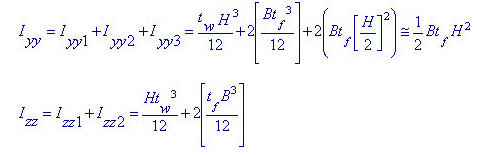
When the width (B) is constant and the height (H) varies, the moment of inertia about the strong axis shows a nearly parabolic variation if the 1st and 2nd terms are neglected in the above equation. The moment of inertia about the weak axis varies almost linearly. Hence, it is feasible to use Iyy Variation = 'Parabolic', Izz Variation = 'Linear'. On the other hand, when the height (H) is constant and the width (B) varies, the moment of inertia about the strong axis varies almost linearly and the moment of inertia about the weak axis shows a nearly cubic variation. Hence, it is feasible to use Iyy Variation = 'Linear', Izz Variation = 'Cubic'.
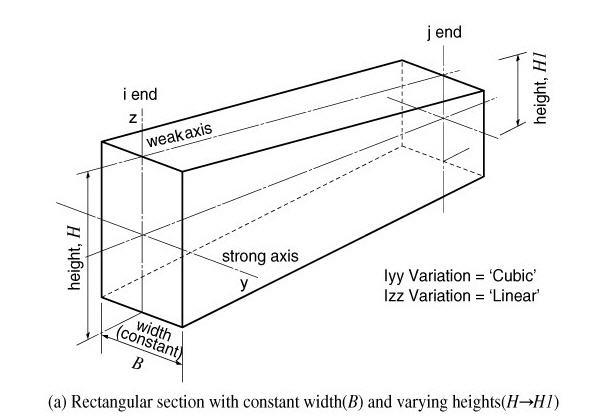
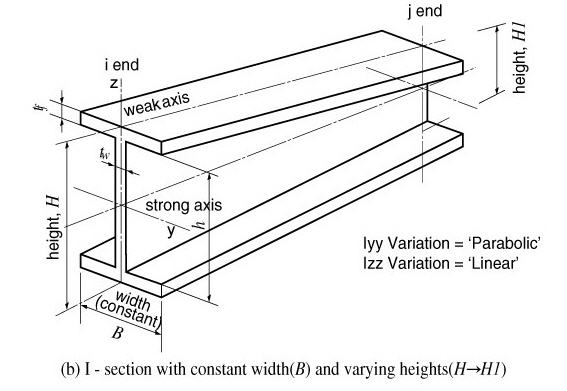
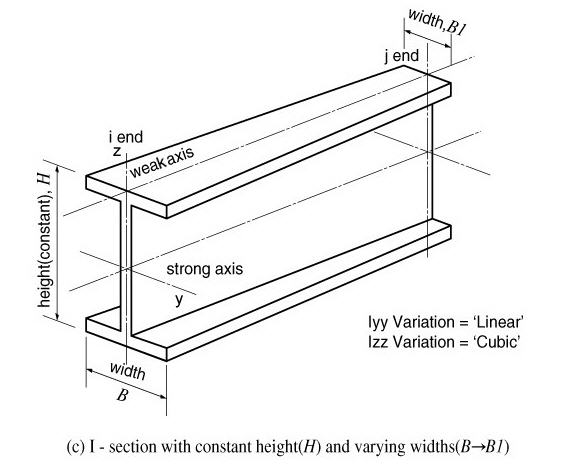
Entry of section data for a tapered section member
Note 2
In the results produced in contours, diagrams and tables, dimensional variation in the axial direction affects the moment of inertia only. In Beam Detail Analysis, section properties are directly calculated at 1/4, 1/2 and 3/4 points using the shape information. As such, dimensional variation affects all the section properties (A, Asy, Asz, Ixx, Iyy & Izz).
-
[Composite tab]
In this dialog box, the sectional data pertaining to the "Analysis considering the section variation before and after composite actions in Composite Bridges" are specified.
Section Type: Assign a section type
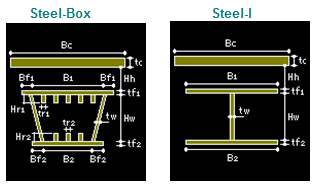
Steel-Box: Structural steel Box Girder
Steel -I: Structural Steel I Shape Girder
User: Section properties defined as General Section in the Value Tab
Slab Width / Girder Num. & CTC
Slab Width: Total width of slab (used for calculating lateral flexure stiffness after becoming composite)
Girder
Num.: Number of girders within the total slab
CTC: Center to center spacing between girders
Note 1
In case when the number of girders is 1 in a structure, enter 1 for Number of girders (Num) and enter 0 for center to center spacing (CTC).
Note 2 When a number of girders exist
If a slab width and girder data are entered where a number of girders exist, the program assumes that the slab acts as a rigid body and increases the moment of Inertia about the vertical direction (Izz). This concept is shown in Case I and Case II below.
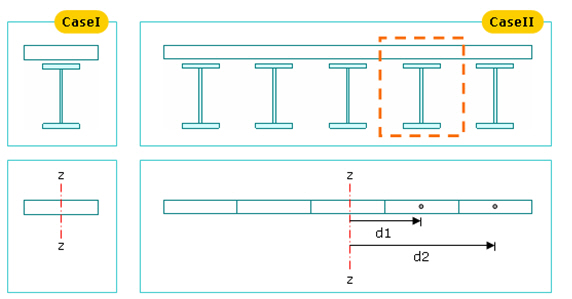
In case of a separate section as in Case I and in case of a rigid body section as in Case II, Izz is calculated as below.
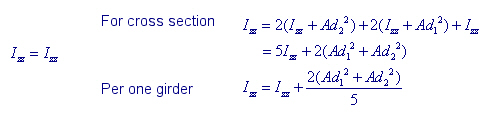
Slab
Bc: Effective slab width for one girder
tc: Thickness of slab
Hh: Distance from the top of girder to the underside of slab
Girder
Hw: Height of web excluding flanges
tw: Thickness of web
B1: Width of top flange (distance between web centers in Box type)
B2: Width of bottom flange (distance between web centers in Box type)
Bf1: Top flange overhang from the center of web in Box type
Bf2: Bottom flange overhang from the center of web in Box type
tf1: Thickness of top flange
tf2: Thickness of bottom flange
N1: Number of stiffeners on top flange
Hr1: Height of top flange stiffeners
tr1: Thickness of top flange stiffeners
N2: Number of stiffeners on bottom flange
Hr2: Height of bottom flange stiffeners
tr2: Thickness of bottom flange stiffeners
Hw: Height of web excluding flanges
tw: Thickness of web
B1: Width of top flange (distance between web centers in Box type)
B2: Width of bottom flange (distance between web centers in Box type)
Bf1: Top flange overhang from the center of web in Box type
Bf2: Bottom flange overhang from the center of web in Box type
tf1: Thickness of top flange
tf2: Thickness of bottom flange
Before(After) Composite
If "User" is selected in Section Type, select Before & After Composite sections.
Section
Select the section data to be applied s Before/After Composite sections from the section data already defined under other tabs such as DB/User, Value, ect.
Material
Click [Select Material from DB...] button to select the material properties for steel and concrete stored in the DB for a country. The following items are automatically entered.
Es/Ec: ModulusRatio, steel to concrete
Ds/Dc: Density ratio, steel to concrete
Note
For the calculation of section properties of Composite Section, concrete is converted into steel. The self-weight is computed as follows:
The Weight of Composite Section = Steel Weight + Concrete Weight
If Ds/Dc = 0, concrete weight is ignored and only steel weight is considered.
Ps: Poisso's ratio of steel
Pc: Poisson's ratio of concrete
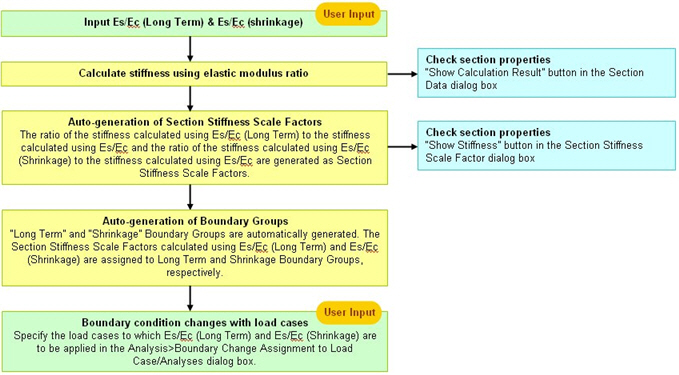
Multiple Modulus of Elasticity
Recalculate the modulus of elasticity of slab concrete to calculate the stresses due to creep and shrinkage. Multiple elastic modulus ratios need to be inputted into an identical section for different load cases. Application of this to analyses and stress checks is specified in EN1994-2 (Eurocode4: Design of composite steel and concrete structures, Part 2) 5.4.2.2.
By checking on this option and entering Es/Ec(Long Term) and Es/Ec(shrinkage), the section properties for post-composite section with those modulus ratios taken into account are calculated.
The value Ixx of the post-composite section is calculated based on the shear modulus ratio (Gs/Gc), not the elastic modulus ratio (Es/Ec). When Es/Ec is entered from DB, Poisson's Ratios from DB are used for the calculation of Gs and Gc. When Es/Ec is inputted by the user, Poisson's Ratio is set to 0.