Global Control for Time History Analysis
Enter the necessary analysis conditions to be applied to time-history analysis. The Followings can be controlled.
1. Geometric Nonlinearity Type: Specify whether the geometric nonlinear effect due to large displacement is considered.
2. Initial Load: Enter the initial load (in general, the gravity loads) for time-history analysis.
From the Main Menu select Load > Dynamic Loads > Time History Analysis Data > Global control > Global control.
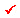 Geometric Nonlinearity
Type
Geometric Nonlinearity
Type
Select Large Displacement to consider the geometric nonlinear effect due to large displacement in time-history Analysis.
 Initial Load
Initial Load
Define, modify or delete the initial load cases, which will be applied prior to time-history analysis.
Perform Nonlinear Static Analysis for Initial Load
This is the general way of applying the initial load.
Import Static Analysis / Construction Stage Analysis Results
1. When the boundary conditions are different between the initial load and the pushover load.
2. To use the result from the final construction stage as the initial load.
Note 1
When using the result from the final construction stage as the initial load for the time-history analysis, the member forces from the construction stage analysis will be imported and nonlinear analysis will not be performed for the initial load.
Note 2
For the following cases, nonlinear analysis will not be performed for the initial load but the result from the static analysis will be imported for the time-history analysis.
- When the boundary conditions/section stiffness scale factors are different between the initial load and the dynamic load.
- When using the member forces from the final construction stage as the initial load for the time-history analysis Type your drop-down text here.
Load Case
Select the load cases, which are to be defined as the initial load for pushover analysis, among the load cases applied to static analysis.
Scale Factor
Enter the magnification/reduction factors to be applied to each selected load case for the initial load.
Note 1
If the following temperature loads are entered as an Initial Load, pushover analysis cannot be performed.
1. Beam Section Temperature
2. Temperature Gradient
3. System Temperature
4. Nodal Temperature
5. Element Temperature
Note 2
The member forces caused by the initial load (in general, the gravity load) are added to the resulting member forces due to pushover analysis. However, the displacements caused by the initial load are not considered in the pushover analysis.
Note 3
If P-M interaction is considered in the hinge properties, it is recommended to apply the initial load.
Note 4
In order to check the results due to initial load in the pushover analysis, a linear static analysis for the load cases which are defined as initial load should be performed.
placement vector after n iterations
Note 2
In general, applying displacement norm is enough. In a very special case, an exact solution is not obtained because of remaining unbalanced force is not negligible although they converge by the displacement norm. In that case, the user may solve the problem by considering additional criteria (force norm and energy norm)
Note 3
When multiple norms are applied, the number of iterations in each increment step increases.
Note 4
When the convergence tolerance is not satisfied, the remaining unbalanced force is added to the external load in the subsequent step. Therefore, if the analysis results are converged in the current step, the failure of convergence in the previous step does not affect analysis results.
Increment Step for Initial Load Case
Increment Stop : Enter the incremental steps until which the load will be incrementally applied to the structure.
For example, if the number of incremental steps and the total load are 100 and 100 ton respectively
in nonlinear static analysis, the load increases by 1 ton, and analysis is carried out for each step.
Result Output
Final Step Only : Output only the result of final step
Step Number Increment for Output : Analysis time step required for producing results of the time history analysis
Results produced at the interval of (Number of Output Steps x Time Increment)
Iteration Parameters
Specify the maximum number of sub-iterations and a tolerance limit for convergence criterion.
Permit Convergency Failure
By increasing the number of steps in an iterative nonlinear analysis, the rate of convergence can be improved. However if the number of steps is large, the analysis could be very time-consuming.
When this option is checked on and if the analysis results do not converge, midas automatically subdivides the step at which divergence occurs. Therefore analysis can be converged without increasing the number of steps. When this option is checked off and if the analysis results do not converge, the analysis will be terminated.
Max. Number of Sub-steps
It is maximum number of Sub-steps, which are segmented from each increment step
Maximum Iteration
Enter the maximum number of sub-iterations in an increment step for repetitive analyses to satisfy an equilibrium condition of the structure.
Convergence Criteria
Specify the basis on which to assess the convergence.
Energy
Norm
Assess the convergence on the basis of
Energy (Member force x displacement) Norm.
Displacement
Norm
Assess the convergence on the basis of
Displacement.
Force
Norm
Assess the convergence on the basis of
Member Force Norm.
Note
The selection of the convergence criteria for repeating or ending
the analysis must be based on the condition to reflect the effects
of various degrees of freedom. For example, in the case of Displacement
Norm, if the displacement resulting from the corresponding analysis
step is {D1}, and the total
displacement accumulated from each step is {D2}, the Norm is expressed
as ![]() . If this value is
smaller than the specified value, a convergence is considered
to have occurred and the program stops the iterative analysis.
. If this value is
smaller than the specified value, a convergence is considered
to have occurred and the program stops the iterative analysis.
Consider ‘Ignore Elements for NL. Analysis Initial Load’
If check this option, The initial load acting on the specified member is ignored in NL. Analysis.
- This option makes the members such as a masonry wall and brace to resist only the force of NL. Analysis without being affected by initial load like a gravity loads
- The member to apply the option can be assigned with the function of the below path.
: Load > Dynamic Loads > Time History Analysis Data > Global control > ‘Ignore Elements for NL. Analysis Initial Load
Nonlinear analysis Result Output Option
- Output the checked results.