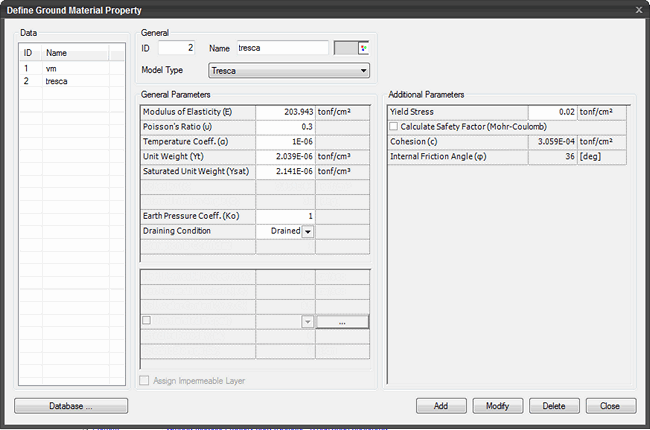
General Parameters
Modulus
of Elasticity (E)
The slope of the stress-strain
line for a linear isotropic material.
Poisson's Ratio (u)
The ratio of the radial
(or lateral) strain to the vertical strain.
Temperature Coeff. (α)
The relative change
of a physical property when the temperature is changed by 1 K.
Unit Weight (Υt)
The weight of soil per unit volume.
Saturated Unit Weight
(Υsat)
The weight of saturated soil per unit volume.
Earth
Pressure Coeff. (Ko)
The ratio of horizontal
principal effective stress to the vertical principal effective stress.
Draining Condition
Drained
Dissipation of pore water pressure takes
place upon the load application.
Undrained
Dissipation of pore water pressure does
not take place upon the load application.
Skempton 'B' Coefficient
Enter the value of
the coefficient for an 'Undrained' condition.
Additional
Parameters
Yield Stress
Uniaxial compressive stress.
Safety Factor Calculation
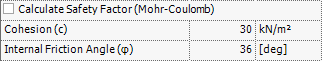
The
safety factor is calculated on the basis of the ratio of the current state
of stress of the material to the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion. The
Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion is most widely used criterion for brittle
materials like ground. SoilWorks uses the criterion
for all the material models in the Tunnel Module.
|