Elastic Ground (Equivalent Linear)
The Elastic Ground (Equivalent Linear) model is used to model the behavior of soil under the action of dynamic loading. Soil behavior changes from linear to nonlinear as the induced shear strain increases from 10^-6 to 10^-3. The soil mass is modeled as a linear mass upto the strain level of 10^-3 and dynamic properties of soil, which are independent of the strain amplitude, are expressed in terms of a linear model.
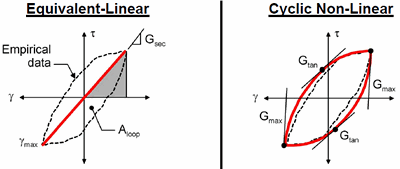
The following image shows the difference between Equivalent-Linear and Cyclic Nonlinear behavior.
Applicable Modules:
Ground |
Slope |
Soft Ground |
Foundation |
Seepage |
Dynamic |
General Parameters
Unit Weight (Υt)
The weight of soil per unit volume.
Additional Parameters
Shear Modulus (G)
It is the dynamic shear modulus. It defines the slope of the hysteresis loop.
Poisson's Ratio (V)
The ratio of the radial (or lateral) strain to the vertical strain.
Damping Ratio
It is a dimensionless quantity which measures the energy lost per cycle os shaking. It defines the breadth of the hysteresis loop.
Strain Compatible Property
The equivalent modulus, G and the equivalent damping (strain-dependent properties) corresponding to the computed shear stains are determined using an iterative procedure based on linear dynamic analysis (equivalent linear method).Dynamic Shear Modulus and Damping are dependent on shear strain levels. The iteration is continued till the modeled strain dependent soil properties are compatible with the strain levels associated with the calculated response of the system.
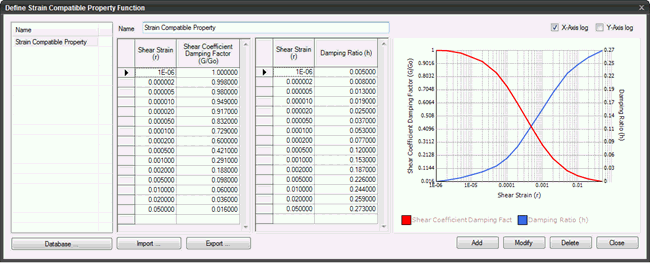
Note: Under the effect of dynamic stresses, soil tends to soften. This is expressed with respect to Gmax. The ratio G/Go decreases with increase in cyclic shear strain.
Note: Due to decrease in the soil stiffness under the effect of cyclic shear strain, damping of the soil mass increases.
Name
Specify the name of the Strain Compatible Property function.
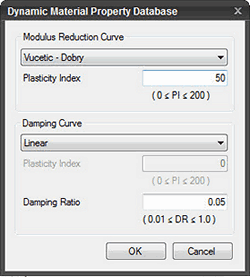
Database
Select the strain compatible property function from the database.
Classification |
Database |
Modulus Reduction Curve |
Clay - Pl=5-10 (Sun et al.0) Clay - Pl=10-20 (Sun et al.0) Clay - Pl=20-40 (Sun et al.0) Clay - Pl=40-80 (Sun et al.0) Clay - Pl=80+ (Sun et al.0) Clay (Seed and Sun 1989) Gravel (Seed et al.0) Linear Rock Rock (Idriss) Sand (Seed & Idriss) - Lower Bound Sand (Seed & Idriss) - Average Sand (Seed & Idriss) - Upper Bound Sand (Seed and Idriss 1970) Vucetic - Dobry |
Damping curve |
Clay - Lower Bound (Sun et al.0) Clay - Average (Sun et al.0) Clay - Upper Bound (Sun et al.0) Clay (Idriss 1990) Gravel (Seed et al.0) Linear Rock Rock (Idriss) Sand (Idriss 1990) Sand (Seed & Idriss) - Lower Bound Sand (Seed & Idriss) - Average Sand (Seed & Idriss) - Upper Bound Vucetic - Dobry |
Note: The user may also input the values to draw Modulus Reduction and Damping curves manually.
Import
Import a *.scp file.
Export
Export a *.scp file.
Log Axis
Specify log scale on X and Y axis.
.gif)