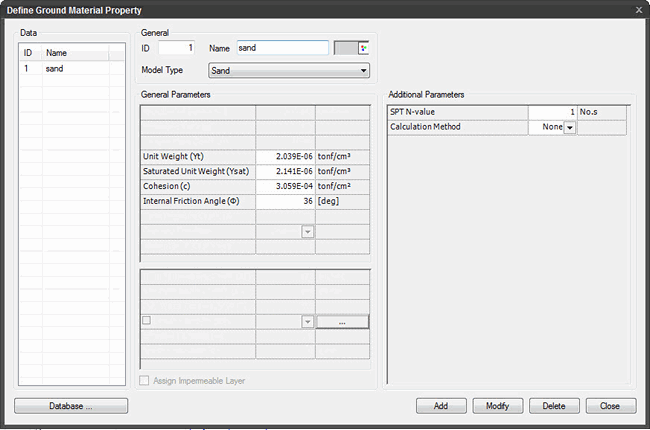
Sand
The Sand model is used to model the settlement of shallow foundations in granular soils. In general, settlement of a foundation has two components-elastic and consolidation settlement. Only the elastic settlement is considered for a foundation supported by granular soils within the zone of influence of stress distribution.
Applicable Modules:
Ground
|
Slope |
Soft Ground |
Foundation |
Seepage |
Dynamic |
General Parameters
Unit Weight (Υt)
The weight of soil per unit volume.
Saturated Unit Weight (Υsat)
The weight of saturated soil per unit volume.
Cohesion (c)
It is a measure of the forces that cement particles of soil.
Internal Friction Angle (Φ)
It is a measure of the shear strength of soils due to friction.
Additional Parameters
SPT N-value
The value for granular soils obtained from the SPT (Standard Penetration Test). It is an in-situ dynamic penetration test which is designed to obtain engineering properties of soil. It is difficult to take undisturbed samples in cohesionless soils hence, an in-situ test like SPT is used to estimate the extent of settlement.
Calculation Method
Method to determine settlement in granular soil.
None
Debeer
The settlement of every layer can be calculated by this method.
The compressibility coefficient C is given by the following relation,
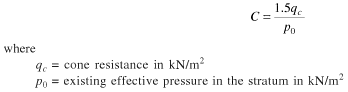
A plot of showing variation of qc with depth is prepared and then it is broken up into different parts each having (almost) equal qc. For each part, po and ∆p are calculated at the centre of a layer and the total settlement is calculated as the sum of individual settlement of each layer.
B.K. Hough
Hough Method is an empirical method for predicting settlements of shallow foundations on cohesionless soils. In this method, subsurface soil profile is divided into layers which are homogeneous with relation to SPT blow count. The SPT blow counts are corrected for overburden stress which is then used to determine bearing capacity index (C'). For each layer, σ'v and ∆σ' are calculated at the centre of a layer and the total settlement is calculated as the sum of individual settlement of each layer.
![]()