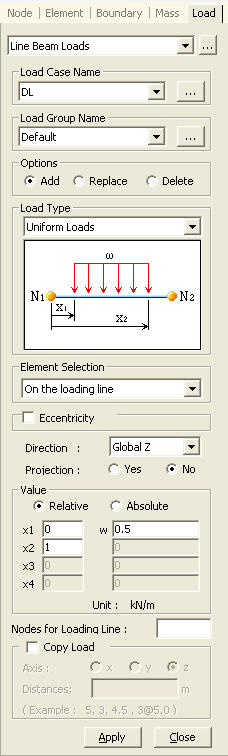
Line Beam Loads
Where several beam elements are continuously connected in a straight line, set the end points of the line and enter the continuous beam load. The load type may be a distributed load or in-span concentrated loads. Modify or delete previously entered loads as necessary. Loads can be also applied to a curved continuous beam, which is located in the plane of the loading direction.
In addition, curvilinear distribution such as earth pressure can be loaded by using curved loads.
Eccentric loads can be applied to beam elements with reference to the GCS or ECS.
From the Main Menu select Load > Line Beam Loads.
Select Static Loads > Line Beam Loads in the Menu tab of the Tree Menu.
|
|
|
 Element Selection
Element Selection
Select the control target for loading the beam loads.
On the loading Line: Line Beam Loads are applied to the elements on a straight line defined by two nodes.
Select Element: Line Beam Loads are applied to the selected elements.
Note
The elements that are subjected to Line Beam Loads must be placed in the plane of the loading direction. Line Beam Loads can be also applied to curved beams provided that the beam lies on the plane.
 Eccentricity
Eccentricity
By assigning the eccentricity distance, the user can easily assign an eccentric load.
As shown in the picture below, by inputting the eccentricity distance and load, the program automatically converts them to an equivalent moment. This function is convenient to assign an eccentric beam load, such as wind load.
Direction: Input the direction of eccentricity
Distance: Input the direction of eccentricity
I-End: Eccentricity from the ![]() node
node
J-End: Eccentricity from the ![]() node
node
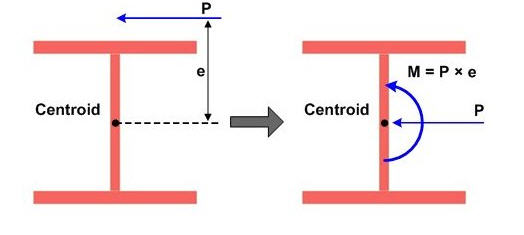
Eccentric Beam Load
 Direction
Direction
Assign the loading direction of continuous beam loads. The loading directions are as follows :
Local x: Beam load applied in the element local x-direction
Local y: Beam load applied in the element local y-direction
Local z: Beam load applied in the element local z-direction
Global X: Beam load applied in GCS X-direction
Global Y: Beam load applied in GCS Y-direction
Global Z: Beam load applied in GCS Z-direction
When the loading direction does not correspond to the above 6 directions, enter the force components in each direction with appropriate signs.
 Projection
Projection
Define if the continuous beam load is to be applied along the continuous beams or if the loading is to be vertically projected on the beams. This command takes effect only when the load type is 'Uniform Loads' or 'Trapezoidal Loads' and the loading direction is 'Global'.
Yes: When a vertically projected continuous beam load is applied to the continuous beams.
No: When a continuous beam load is applied along the continuous beams.
 Value
Value
Define if the loading positions of the continuous beam loads are to be entered in the relative ratio of a loaded beam length.
Relative: Relative ratio of a beam length
Absolute: Real beam length
x1, x2, x3, x4, W: Refer to the guide diagram to specify the load magnitude and locations.
a, b, c: Constants defining the load distribution equation
When the Curved Load Type is selected, curvilinear distribution is given by
P(x)=ax^0.5+b
P(x)=ax^2+bx+c

 Nodes for Loading Line
Nodes for Loading Line
Enter the node numbers of the two ends of the continuous beams. The two node numbers may be set with the mouse using Node Snap in the working window.
 Copy Load
Copy Load
Check in copy load to repeat the continuous beam loads for other rows of continuous beams.
Axis: Set the copy direction
x: UCS x-direction
y: UCS y-direction
z: UCS z-direction
Distances: Copy distances
When copying loads onto several rows of other continuous beams, enter the copy distances (spacings) as many times as required.
(Ex. 5.0, 3.0, 4.5, 3@5.0)