Name
Enter the name of the convection
condition.
Type
Select the type of target
objects to which convective heat transfer conditions will
be applied. Face, 2D Element, 3D Element Face and
3D Element Free Face can be selected.
Ambient
Temperature
Enter the ambient temperature
value for the selected target objects.
By Value
Enter
the ambient temperature directly.
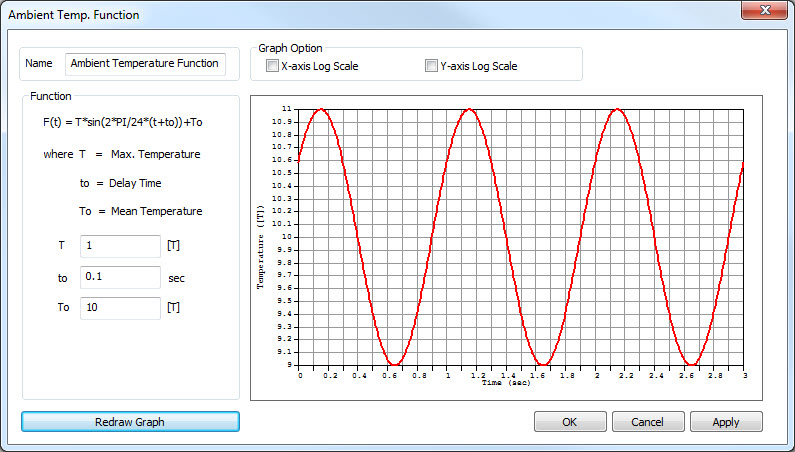
Ambient Temp. Function
In
the ambient temperature function, you can define the outside
temperature using Sine function, where
T:
Maximum outside temperature,
to: Delay time, and
To: Minimum outside
temperature.
Convection
Coefficient
Enter
the convection coefficient.
Base
Function
Set a spatial function or a non-spatial
function as a base function to be applied to the magnitude
of convection or temperature.
Time Function
Select the function to be applied
to time.
Global Time
The time applied to the time function
is based on the total analysis time.
Local Time
The time
applied to the time function is based on the subcase time.
Thermal
Load
Register
the specified convection conditions to a desired thermal
load set.
The user may assign any name to the load set. |