Settlement Load Cases
| ||
|
| ||
|
| ||
|
Enter the settlement load cases for support settlement analysis.
The procedure for settlement analysis in MIDAS/Gen is as follows:
1. Enter the support settlement groups, which will be likely subjected to simultaneous settlements and the corresponding magnitudes in the Load>Settlement Analysis Data>Settlement Group menu.
2. Define individual Settlement Load Cases for relevant settlement groups in Load>Settlement Analysis Data>Settlement Load Cases. 3. Click the Analysis>Perform
Analysis menu or
4. Upon successfully completing the analysis, we can check the maximum and minimum values computed for the number of possible support settlements. We may also combine the results with the results of other load cases. | ||
|
| ||
|
| ||
|
| ||
|
From the Main Menu select Load > Settlement Analysis Data > Settlement Load Cases.
Select Settlement Analysis Data > Settlement Load Cases in the Menu tab of the Tree Menu. | ||
|
| ||
|
| ||
Operations
View by Max Value Item (with concurrent forces)
Settlement Analysis generates the most critical forces by components (Fx, Fy, Fz, Mx, My and Mz) out of all the load cases of Specified Displacements of Supports defined by the user. The element force components are non-concurrent, which belong to different load cases.
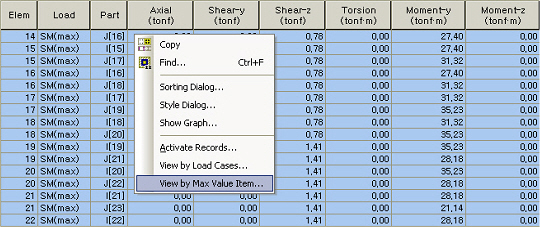
Beam Force Table of maximum non-concurrent forces
In order to design members, concurrent forces are required. The View by Max Value Item (invoked upon right-clicking on the table) provides
the concurrent forces. The concurrent forces correspond to the maximum / minimum force component in the Component column in the table.
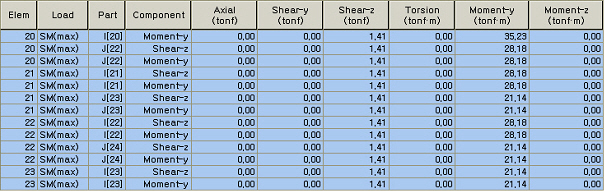
Concurrent Force Table
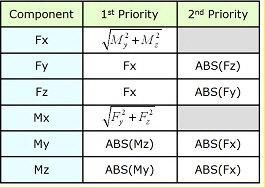
In case Max or Min member forces are the same under 2 or more load cases, the corresponding concurrent forces are tabulated by the priority shown in the table below. For example, when two or more settlement load cases produce a same maximum Fx in an element, the concurrent forces are tabulated for the settlement load case, which produces the largest value of SQRT(My^2+Mz^2).
| ||
|
|

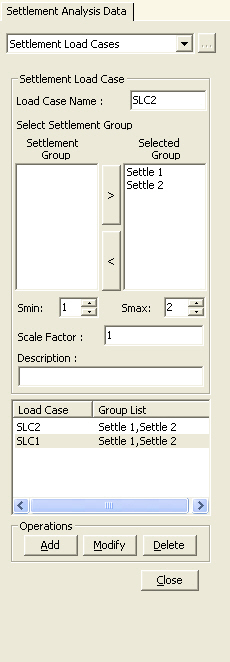
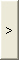 to include them in the Selected Group.
When previously selected support settlement groups are to be excluded,
first assign the support settlement groups and click
to include them in the Selected Group.
When previously selected support settlement groups are to be excluded,
first assign the support settlement groups and click 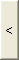 to
remove them from the Selected Group.
to
remove them from the Selected Group.