Tendon Property
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Define the tendon properties such as tendon area and instantaneous prestress losses. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
From the Main Menu select Load > Prestress Loads > Tendon Property.
Select Static Loads > Prestress Loads > Tendon Property in the Menu tab of the Tree Menu. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
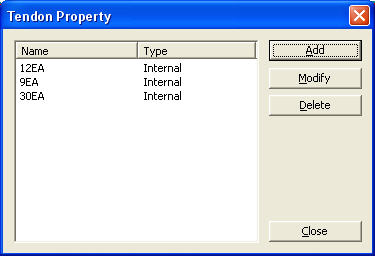
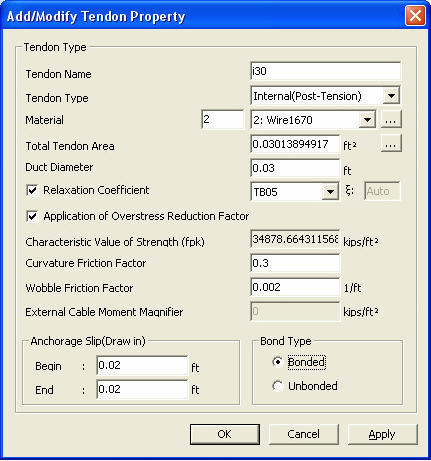
To define new or additional tendon properties
Click
Add/Modify Tendon Property dialog box
Tendon Name
tendon name being defined
Tendon Type
Define the tendon type among Pre-Tension, Post-Tension and External.
Internal (Pre-Tension): Prestressing tendons prior to casting concrete, which transmits prestress through bonding between concrete and tendons
Internal (Post-Tension): Post-tensioning tendons through hardened concrete members ?tendons are gradually stressed and anchored to the members.
External: Tendons are placed external to concrete members and stressed.
Note
1
Note
2
Material
Select the material properties of the tendon.
Click
Total Tendon Area
Specify the total area of the tendon. You
may either directly specify the cross-sectional area or click
Duct Diameter
When the Tendon Type is Post-Tension, input for the diameter of duct is required. Based on the tendon area, the duct diameter is automatically calculated, which is then referred to for duct diameter input.
Strand Diameter
When the Tendon Type is Pre-Tension, the diameter of strand should be entered. The program automatically calculates the diameter of strand corresponding to the specified Total Tendon Area. The diameter of the strand is used to compute Transfer Length.
Relaxation Coefficient: C
Select Magura or CEB-FIP for the method of applying relaxation. To ignore the steel relaxation, uncheck the box.
Revision of V.7.6.0
Curvature Friction Factor
to account for friction loss due to the curvature of tendons
Wobble Friction Factor
To account for straightness/length effect (imperfection in alignment along the length of tendon, regardless of straight or draped alignment)
Ultimate Strength
Yield Strength
External Cable Moment Magnifier
Enter the increase of effective prestress of external cable to be used for calculating failure-resisting moment. Entered stress increase will be used for PC design.
Anchorage Slip (Draw in)
Tendon slippage at the anchor
Begin: slippage at the beginning of tendon if tensioned here
End: slippage at the end of tendon if tensioned here
Bond Type
Bonded: Section properties reflect the duct area after grouting
Unbonded: Section properties exclude the duct area.
To modify the previously entered tendon data Select the tendon from the list in the Tendon
Property dialog box and click
To delete the previously entered tendon data Select the tendon from the list in the Tendon
Property dialog box and click
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 in the Tendon Property
dialog box and enter the following:
in the Tendon Property
dialog box and enter the following: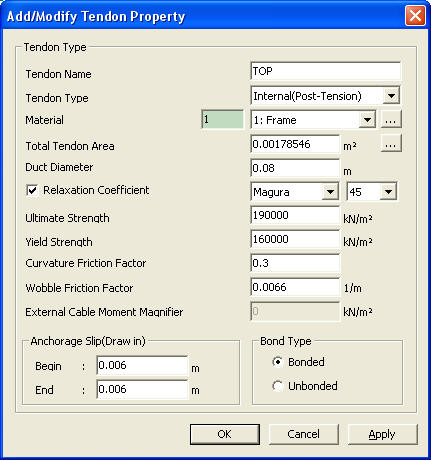
 Display.
Display. to the right to add new or modify/delete previously
defined tendon properties.
to the right to add new or modify/delete previously
defined tendon properties.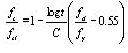
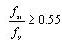 ,
,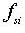 : initial
stress,
: initial
stress,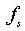 : stress
at time
: stress
at time 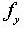 : yield stress
(0.1% Offset Yield Stress)C: Relaxation Coefficient (general steel: 10,
low-relaxation steel: 45)
: yield stress
(0.1% Offset Yield Stress)C: Relaxation Coefficient (general steel: 10,
low-relaxation steel: 45)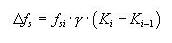
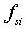 : initial stress,
: initial stress,
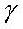 : final loss ratio due to steel relaxation,
: final loss ratio due to steel relaxation, 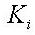 : progress of steel relaxation at the last time step
: progress of steel relaxation at the last time step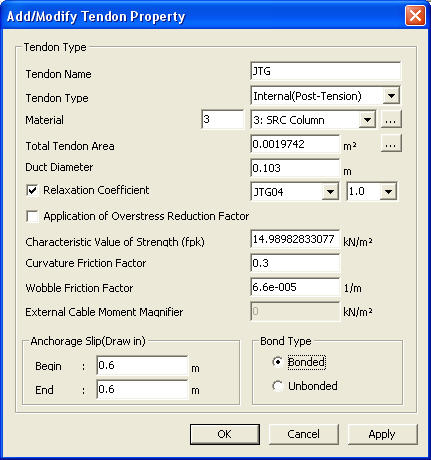
 to change any relevant data.
to change any relevant data. to eliminate any relevant
data.
to eliminate any relevant
data.