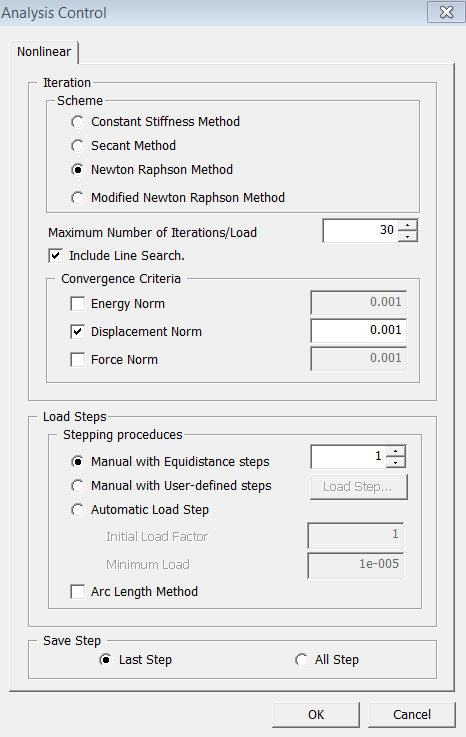
Analysis Control - Nonlinear Static

<Analysis Control-Nonlinear>
Scheme
Specify non-linear analysis method
Constant Stiffness Method
A method of convergence towards the solution with the constant stiffness during the iterative analysis process. The constant stiffness refers to the elasticity.
Secant Method
A method of convergence towards the solution by the origin direction stiffness during the iterative analysis process.
Newton Raphson Method
A method of convergence towards the solution by the tangent stiffness of the load-displacement diagram during the iterative analysis process.
Modified Newton Raphson Method
A method of executing the current stage iterative analysis by using the stiffness of the previous stage load step
Maximum Number of Iterations/Load Step
Maximum number of iterations for analysis per
Load Step.
Include Line Search
When performing iterative methods, the include line search is an algorithm which accelerates the speed of convergence. However, in cases of
material non-linear analysis, the speed may be reduced significantly.
Convergence Criteria
Specify
the basis on which to assess the convergence. If multiple criteria are
chosen, then all of them must be satisfied to establish the convergence.
Energy Norm
Assess
the convergence on the basis of Energy (Member force x displacement) Norm.
Displacement Norm
Assess
the convergence on the basis of Displacement Norm.
Force Norm
Assess
the convergence on the basis of Member Force Norm.
Stepping procedures
Setting the load step process
Manual with Equidistance Steps
The load are
divided into a number of increments based on the number of load increments.
Summation of load factor must equal to one.
User Defined Steps
Load increment size can be manually inputted by user. Negative Load factors or factors greater than one can be inputted.
Automatic Load Step
Automatic load steps are calculated by the solver. If a particular stages fails to converge, the initial load factor is reduced by 25% and the analysis is performed again using the reduced load increment. Analysis will terminate if the load factor is less than the minimal load factor or if the number of iterations is greater than the assigned value.
Arc Length Method
In the load-displacement diagram, the Arc Length Method recognizes length increments of the segment as an arc length, and this method, by putting a limit to the specified length, finds the nonlinear solution.
Save Step
Specify
options for saving result data.
Last Step
This
option saves only the last load step in the result file.
All Step
This
option saves all the load steps in the result file.
User Defined Load Step
The above defined Iteration Method is applied individually to load cases.
Skip Nonlinear Analysis
It perform true linear analysis, not repeating the processes of nonlinear analysis.
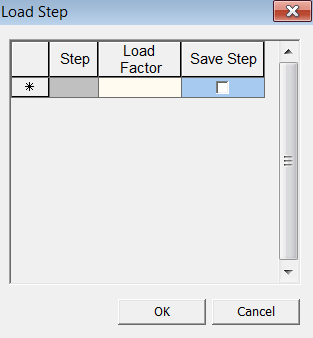
<Add/Modify Analysis Case-Static-User Defined Load Step>
Step
Number
of Load Steps entered.
Load Factor
Load
factors for each increment.
Save Step
It saves
the result data in the output file at the stage.