Element Definition

midas FEA provides various types of elements. Each element type is defined by the structural characteristics of its engaged nodes.
-
Scalar Element
The scalar element consists of 1 or 2 node(s) and it does not have a geometrical characteristic. The spring element falls into this category.
-
1D Element (Line)
The 1-dimensional element has a geometrical characteristic of length and consists of 2 or 3 nodes. The truss and beam elements fall into this category.
-
2D Element (Plane)
The 2-dimensional element, which represents either triangular or quadrilateral element, has the geometrical characteristic of area. Plane Stress Elements, Plain Strain Elements, Axisymmetric Elements and Plate Elements fall into this category.
-
3D Element (Solid)
The 3-dimensional element has a geometrical characteristic of volume. Tetrahedron, Pentahedron (Wedge or Prism) and Hexahedron (Brick) fall into this category.
-
Miscellaneous
A few other element types, such as Rigid Links and Reinforcements, fall into this category.
In midas FEA , the element types are categorized by their geometrical characteristic, and the structural behavior of elements may be different within the same category (Ex. Truss and Beam).
midas FEA provides the element type of Plot 1D and Plot 2D. When actual elements for analysis are created from extrusion of lower dimensional elements, the user can apply these element types to the lower dimensional elements. The Plot 1D and Plot 2D elements are automatically eliminated from the analysis so that the user does not have to delete the lower dimensional elements.
In reality, a structure always exists in a space and it can be modeled by any type of element(s) with proper dimensions. Its structural behavior can be expressed with an accurate material model and geometrical property. To construct an analysis model of the structure, its elements must include these 3 important characteristics: 1) nodal connectivity, 2) material property and 3) additional geometric property, such as thickness.
The geometric properties that are required to be defined in each 1D, 2D and 3D element are listed in the following table.
|
Element Type |
Geometric Characteristic |
Additional Property for Volume Calculation |
|
1D |
Length (L) |
Area (A) |
|
2D |
Area (A) |
Thickness (t) |
|
3D |
Volume (V) |
N/A |
![]() The above table is should be used to understand the basis of geometric property. The list only contains the common items. Depending on its structural behavior, each element type may require additional properties.
The above table is should be used to understand the basis of geometric property. The list only contains the common items. Depending on its structural behavior, each element type may require additional properties.
Element is defined by two characteristics, Property and Material.

<Relation Tree of Element, Property, and Material>
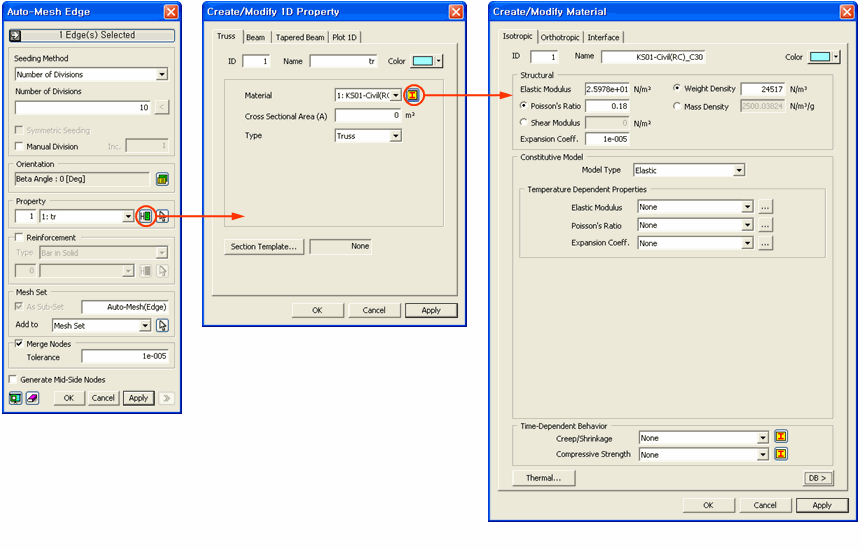
<Example of Dialog Boxes for defining Element, Material, and Property>