 Revision of Ver.7.4.1
Revision of Ver.7.4.1 Revision of Ver.7.4.1
Revision of Ver.7.4.1Function
Produce a detail deformed shape, SFD/BMD, maximum stress distribution and sectional stress distribution diagrams for a particular section.
Call
From the Main Menu select Results > Beam Detail Analysis.
Select Results > Beam Detail Analysis in the Menu tab of the Tree Menu.
Usage
Select a desired load case or load combination.
Click to the right to enter new or modify existing load combinations. (Refer to "Load Cases / Combinations")
 Element Number
Element Number
Enter the element number for which a detail analysis is desired, or click
the element number entry field and the relevant beam element in the working
window.
Note
Beam Detail Analysis finds forces for moving load cases, load combinations
including moving loads and envelope load cases by interpolating the values
at i, 1/4 points, midpoint and j node.
.jpg)
When the element is assigned, the following results window is displayed.
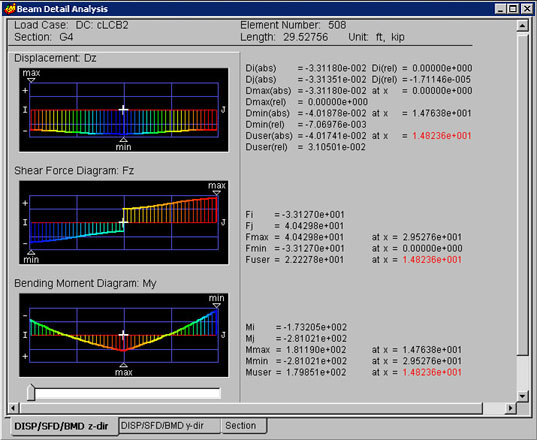
Produce deformed shape, SFD and BMD for the beam element's strong axis
Displacement:
Dz
Deflected shape in the element's local z-direction and the corresponding
numerical values
Di (abs) : Absolute displacement at node i (N1)
Dj (abs) : Absolute displacement at node j (N2)
Di (rel) : Relative displacement at node i (N1)
Dj (rel) : Relative displacement at node j (N2)
Note
The relative displacement is obtained by setting the smaller displacement
of nodes i or j to 0 (zero) and calculating the relative displacement
of the other node.
Dmax (abs) : Maximum absolute displacement and the position
Dmax (rel) : Maximum relative displacement
Dmin (abs) : Minimum absolute displacement and the position
Dmin (rel) : Minimum relative displacement
Duser (abs) : Absolute displacement and the position at the location assigned by the user
Duser (rel) : Relative displacement and the position at the location assigned by the user
Note
Move the mouse cursor to the left or right in the displacement graph or
use the slide button at
the bottom of the results
window to assign the position of interest.
Shear Force Diagram: Fz
Shear force in the element's local z-direction and the corresponding numerical
values
Fi: Shear force at node i
Fj: Shear force at node j
Fmax: Maximum shear force and the position
Fmin: Minimum shear force and the position
Fuser: Shear force and the position at the location assigned by the user
Bending Moment Diagram: My
Bending moment about the element's local y-axis and the corresponding values
Mi: Bending moment at node i
Mj: Bending moment at node j
Mmax: Maximum bending moment and the position
Mmin: Minimum bending moment and the position
Muser: Bending moment and the position at the location assigned by the user
Produce the deformed shape, SFD and BMD for the beam element's weak axis
Displacement:
Dy
Deflected shape in the element's local y-direction and the corresponding
numerical values
Shear Force Diagram: Fy
Shear force in the element's local y-direction and the corresponding numerical
values
Bending Moment Diagram: Mz
Bending moment about the element's local z-axis and the corresponding numerical
values
Entry
Section
Stress
Select a stress component and the corresponding member force components
in the dialog bar of Beam Detail Analysis and click .jpg) .
.
Stress components
Normal
Stress in the element's local x-direction ()
Axial stress + Bending stresses due to My and Mz
Tau-xy: Shear stress in the element's local y-direction ( )
Tau-xz: Shear stress in the element's local z-direction ( )
von-Mises
von-Mises Stress =
where,
: Maximum principal stress
: Minimum principal stress
Tresca
Tresca Stress =
Member Force Components
Fx: Axial force in the element's x-direction
Fy: Shear force in the element's y-direction
Fz: Shear force in the element's z-direction
Mx: Torsional moment about the element's x-axis
My: Bending moment about the element's y-axis
Mz: Bending moment about the element's z-axis
Output
Longitudinal
Maximum Stress
Provide the maximum and minimum distribution diagram and the corresponding
numerical values for the assigned stress component along the length of
a beam.
Sig-i:
Maximum section stress at node i (N1) (.jpg) )
)
Sig-j:
Maximum section stress at node j (N2) (.jpg) )
)
Sig-max:
Maximum stress and the position (.jpg) )
)
Sig-min:
Minimum stress and the position (.jpg) )
)
Sig-user:
Maximum stress at the location assigned by the user (.jpg) )
)
Note
Move the mouse cursor to the left
or right in the maximum stress
graph to assign the position
of the stress to be checked.
Cross Section
Stress
Display the stress distribution and the corresponding values for a particular
section of the beam element.
Sig-max:
Maximum stress and the position in the section (.jpg) )
)
Sig-min:
Minimum stress and the position in the section (.jpg) )
)
Sig-user:
Stress at the position assigned by the user (.jpg) )
)
Assign the desired position (on the element's local y-z plane) in the section stress distribution diagram by moving the mouse cursor to the left or right and up or down. In addition, assign the desired position along the length (in the element's local x-axis) by moving the mouse cursor to the left or right in the maximum stress graph.
Location
abs: Distance from the i node to the position assigned by the user
rel (X/L): Distance ratio relative to the total length for the position assigned by the user
Applied Forces/Moments [Fx, Fy, Fz, Mx, My, Mz]: Member forces at the position along the length assigned by the user
 Revision of Ver.7.4.1
Revision of Ver.7.4.1Note
When stress checks are required for a tapered section, its section information such as DB/User and PSC(DB) types is required to produce stresses at the positions (1/4, 1/2 & 3/4). In contours, diagrams and tables, section properties at the positions (1/4, 1/2 & 3/4) are obtained by interpolation between i-end and j-end. Whereas in Beam Detail Analysis, the section properties at the positions (1/4, 1/2 & 3/4) are re-calculated using the section shape information at the corresponding positions. If section properties are not defined in a section, stress results will not be generated.