Select
the node where the load will be applied and specify the
direction. The load size is applied by multiplying the
time function (load size by time) and each load component
(scale factor).
[Object]
The
applied load is defined on the node , but the selection
target can also be set as a geometry shape (edge, surface
etc.) or using auto-select free face nodes. For a line
or surface, the selected shape must have been used for
element creation and the force is applied to all nodes
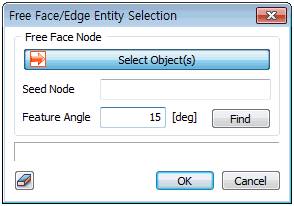
in the specified direction/size. For free face nodes,
select a free face node and all points that make contact
with the node-containing element at an angle smaller than
the specified angle (feature angle) will be automatically
selected.
[Reference
Object]

The
load direction can be set using different methods. The
default input reference is the Global rectangular(cylindrical)
coordinate axis. Geometry shapes (Edge and Surface) can
be selected as a reference direction. Selecting
'Line' or 'Surface' displays the coordinate system of
the selected shape and the load is set with reference
to that system. 'Vector' is used to specify the load direction
using X,Y,Z vector components.
[Components]
Input
the load scale factor according to the set direction.
Generally, the load size is pre-defined as a time variant
value in the time function, and if the maximum ratio value
is defined as 1, the actual load size is input in the
time function. A positive (+) value applies the load in
the set direction and a negative (-) value applies the
load in the opposite direction to the set direction. The
load size change, depending on the coordinate value increase
in the global coordinate system (GCS), can be defined
using a reference function. Here, the input value is multiplied
by the function value for application.
[Time
Dependency (Time function)]
Define
the load size change with respect to time.
Select
the  button to add (select)
a time forcing function. It can only be applied when the
time forcing function data type is 'Acceleration', 'Velocity',
'Displacement', ‘Force’ and ‘Moments’. button to add (select)
a time forcing function. It can only be applied when the
time forcing function data type is 'Acceleration', 'Velocity',
'Displacement', ‘Force’ and ‘Moments’. |
