 Revision of Ver.7.4.1
Revision of Ver.7.4.1 Revision of Ver.7.4.1
Revision of Ver.7.4.1Function
Using the interaction of the base shear and the displacements calculated from the results of a Pushover analysis, the capacity curve and capacity spectrum of a structure are calculated. The demand spectrum is also generated for a design seismic load using the design response spectrum.
The Performance Point, which represents the state of maximum inelastic capacity of the structure, is found through the cross point of the Capacity Spectrum and Demand Spectrum for a given damping ratio.
Call
From the Main Menu select Design > Pushover Analysis > Pushover Curve.
Usage
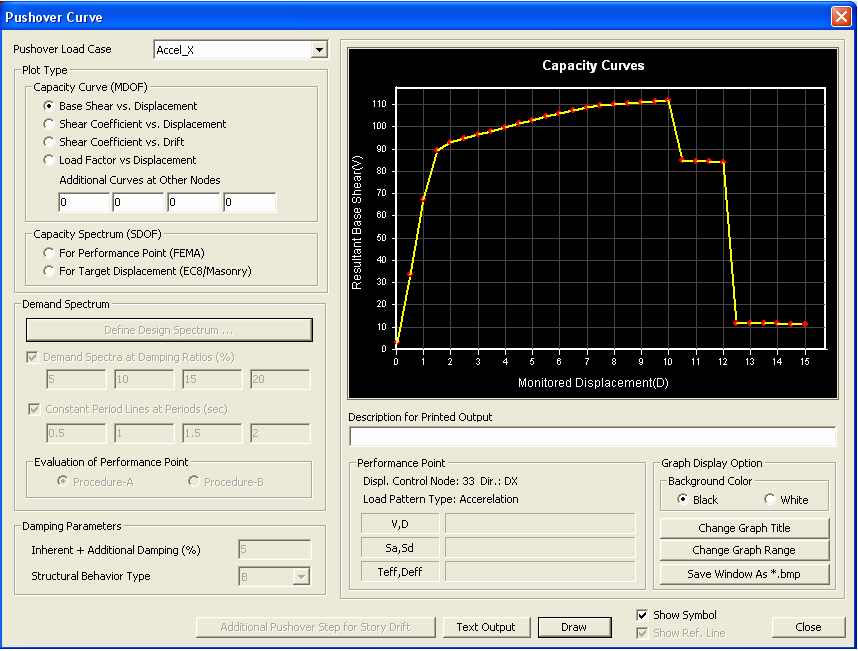
Pushover Curve dialog box
 Pushover Load Case
Pushover Load Case
Select a load case applied to pushover analysis.
Note
If Pushover Load Case acting in GCS Z-direction is specified, only Load Factor vs. Displacement becomes activated in Plot Type.
 Plot Type
Plot Type
Select the type of pushover result curve to be produced.
Capacity Curve (MDOF)
Base Shear vs. Displacement
Shear Coefficient vs. Displacement: Shear coefficient (Lateral load/Total weight) vs. Displacement
Shear Coefficient vs. Drift: Shear coefficient vs. inter-story Drift
Load Factor vs. Displacement
Note 1
If Load Factor vs. Displacement is specified in Plot Type, Capacity Spectrum becomes inactivated.
Note 2
Pushover Curve due to vertical (gravity) load can be produced. An example of application may be an arch structure subjected to vertical displacement in relation to the total reaction.
Additional Curves at other Nodes: Nodes numbers for which additional curves will be produced
Capacity Spectrum (SDOF)
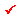
For Performance Point (FEMA) : Load (Base Shear) - Displacement of the pushover analysis is transformed into the Spectral Acceleration (Sa) vs. Spectral Displacement (Sd) curve.
For Target Displacement (EC8/Masonry): Target displacement is a the seismic demand derived from the elastic response spectrum considered in terms of the displacement of an equivalent single-degree-of-freedom system.
กแ When Capacity Spectrum (SDOF) : For Performance Point (FEMA) is selected
 Demand Spectrum
Demand Spectrum

In order to apply the design response spectrum to prepare the demand spectrum, define a design spectrum specified in a design standard.
Demand Spectra at Damping Ratios (%)
Using the specified damping ratio, produce the demand spectrum.
Constant Period Lines at Period (sec)
Produce the corresponding period lines for the specified periods.
Evaluation of Performance Point
Using the effective damping ratios suggested in ATC-40, evaluate the inelastic demand spectrum and compare it with the capacity spectrum to find the performance point.
Procedure-A: The effective damping ratio for inelastic behavior of a structure is evaluated first, and a corresponding demand spectrum is created. The performance point is found through a repetitive process.
Procedure-B: Assuming the ductility demand curve and using the corresponding effective period and effective damping ratio, the path of the performance point is evaluated and the intersection with the capacity spectrum is found.
 Damping Parameters
Damping Parameters
Enter the parameters determining the effective damping ratio.
Inherent + Additional Damping (%)
Specify the total damping ratio (%) reflecting the inherent damping ratio and additional damping resulting from physical devices installed in the structure.
Structural Behavior Type
Select A, B or C to obtain a reduction factor applicable for effective damping.
Note
Structural Behavior Type is classified in the table below.
|
Shaking Duration |
Essentially New Building |
Average ExistingBuilding |
Poor ExistingBuilding |
|
Short |
Type A |
Type B |
Type C |
|
Long |
Type B |
Type C |
Type C |
For example, if 5% is specified for the damping of the structure, the effective damping becomes,
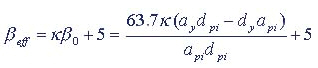
Refer to ATC40 for the definitions of the variables.
 Performance Point
Performance Point
It provides the information on the performance point on the spectrum and the performance point transformed into a multi-degree of freedom system.
V, D
Maximum base shear and maximum displacement of the inelastic structure by the performance point
Sa, Sd
Spectral Acceleration (Sa) and Spectral Displacement (Sd) at the performance point
Teff, Deff
Inelastic effective period and effective damping at the performance point
กแ When Capacity Spectrum (SDOF) : For Target Displacement (EC8 / Masonry) is selected
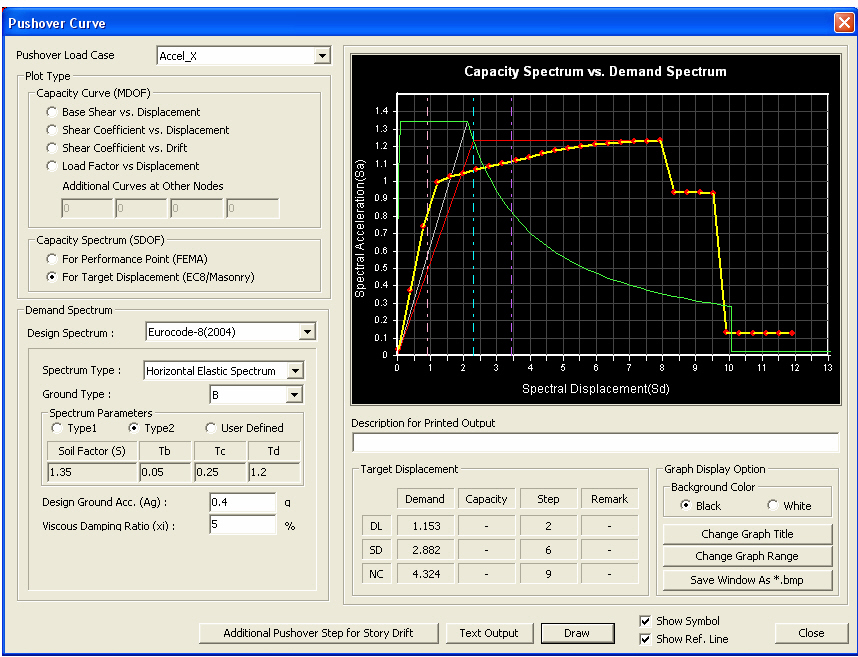
 Demand Spectrum
Demand Spectrum
Design Spectrum: Select the design spectrum (i.e.= The elastic response spectrum associated with a reference return period of 475 years) to be applied to calculate the target displacement for the Limit State of Significant Damage (SD).
Eurocode-8(2004)
User Defined: Predefined user-defined response spectrum function can be selected.
 Target Displacement
Target Displacement
The target displacement of a structure is determined through the transformation to an equivalent single degree of freedom system. For the detailed formula, refer to ANNEX B DETERMINATION OF THE TARGET DISPLACEMENT FOR NONLINEAR STATIC (PUSHOVER) ANALYSIS, EN 1998-1:2004. The target displacement, which is obtained from the above, corresponds to the seismic demand of the Limit State of Significant Damage (SD). Target displacement of the Limit State of Near Collapse (NC) is taken equal to that of SD multiplied by 1.5. Target displacement of the Limit State of Damage Limitation (DL) is taken equal to that of SD divided by 2.5.
Note
When transforming MDOF system to SDOF system, midas applies different modal participation factor to each direction for the 3 dimensional structure. The direction of each mode is determined based on the maximum Modal Participation Mass. For example, if Modal Participation Mass is as follows, Modal Participation Factor for mode 1 and 2 is applied to X-direction and Y-direction, respectively.
|
Mode |
Modal Participation Mass (%) | ||
|
TRAN-X |
TRAN-Y |
ROTN-Z | |
|
1 |
66.23 |
15 |
3 |
|
2 |
13 |
60.85 |
1.06 |
|
3 |
5 |
7 |
45 |
Demand: Roof displacement corresponding to the target displacement for the seismic action is considered. Note that this is the target displacement for the MDOF system, while the vertical lines on the pushover curve represent the target displacements for the equivalent SDOF system.
Capacity: Global capacity of the masonry structure in terms of roof displacement (Master node). Only applicable to Masonry material models.
Global capacity of the Limit State of Significant Damage (SD) is taken equal to the roof displacement at which total lateral resistance (base shear) has dropped below 80% of the peak resistance of the structure, due to progressive damage and failure of lateral resisting elements.
Global capacity of the Limit State of Damage Limitation (DL) is taken as the minimum value between a) displacement corresponding to the maximum base shear in the pushover curve and b) displacement corresponding to the story drift of 3/1000.
Step: The nearest increment step to the target displacement
Remark: Assessment of the result in terms of the global response for the masonry structure. Only applicable to Masonry material models.
Limit
State of SD: The assessment is OK if the global capacity of the
Limit State of SD is greater than the target displacement of the Limit
State of SD 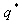 and is
less than 3.
and is
less than 3.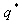 is
the ratio between the acceleration in the structure with unlimited elastic
behavior
is
the ratio between the acceleration in the structure with unlimited elastic
behavior 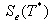 and
in the structure with limited strength
and
in the structure with limited strength 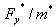 .
.

Limit State of DL: The assessment is OK if the global capacity of the Limit State of DL is greater than the target displacement of the Limit State of DL (i.e.= Target Displacement of the Limit State of SD divided by 2.5.
 Additional Pushover Step for
Story Drift
Additional Pushover Step for
Story Drift
Define the additional pushover steps in order to check the pushover analysis results for the steps which have not been defined in Pushover Load Case. [Details…]
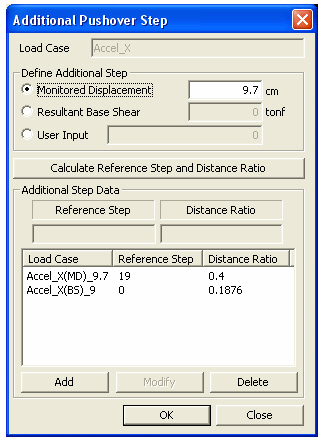
Load Case : The pushover load case defined in Pushover Curve is displayed.
Define Additional Step : Select the method to define additional steps.
Monitored Displacement : Define additional steps based on the displacement.
Resultant Base Shear : Define additional steps based on the base shear.
User Input : Define the additional step name, Reference Step and Distance Ratio directly.
Note Check pushover analysis results for additional steps Additional Step
Entered additional step can be checked in Deformed Shape and Story Drift.
Calculate
Reference Step and Distance Ratio : Click  button
in order to define an additional step by entering Distance Ratio from
the Reference Step to the additional step.
button
in order to define an additional step by entering Distance Ratio from
the Reference Step to the additional step.
Additional Step Data : Determine the displacement of additional step
Load Case : Load case name for which an additional step is added.
Reference : Reference pushover step to determine the position of an additional step
Distance Ratio : Displacement ratio of the reference step to the additional step
 Text Output
Text Output
Pushover analysis result graphs can be saved as text files.
Note
When Performance Point is found, an additional step for Performance Point is added in text file.
 Draw
Draw
Display Capacity Spectrum produced by Performance Point / Target Displacement.
Note
If the user click on Draw button, an additional step for Performance Point is added into Additional Step dialog box.
 Graph Display Option
Graph Display Option
|
|
Background Color Set the background color for the plotted graph. Black: Set the background to black. White: Set the background to white. Change Graph Title The graph title can be changed. Change Graph Range Define the ranges of the X & Y-axes. Save Window As *.bmp Save the graph in the graphic file format of BMP. Show Symbol Display each increment steps in Pushover Curve. Show Reference Line Display the demand corresponding to DL, SD & NC of Target Displacement in Pushover Curve.
|