Wind Loads
In midas Gen, the automatic data entry of wind loads according to various standards is applicable for common buildings where each story can be defined and can reasonably act as a rigid diaphragm. The following procedure is observed :
-
Model the structure.
The structure must be modeled so that the gravity acts in the direction opposite to the GCS Z-direction.
-
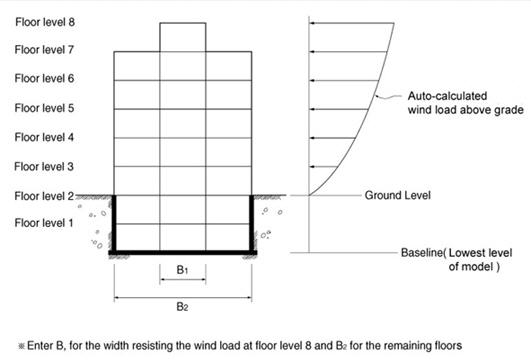
Use Building > Control Data to define the elevation of ground level in GCS Z-axis coordinate.
When the ground level is entered, the parts below this level are considered as underground stories and neglected in the wind load calculation. If the ground level is not specified, the lowest part of the modeled structure is assumed to be the ground level by default.
-
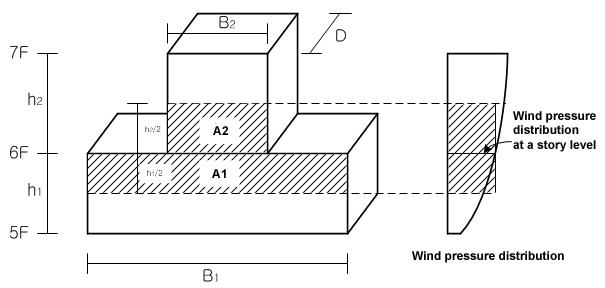
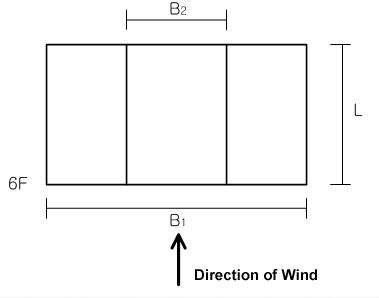
Use Story to define stories and their floor rigid diaphragm characteristics. Enter the application position of wind loads and the width of the story subjected to pressure to generate the wind load at each story.
It is recommended that ![]() be used to auto-generate the data necessary for the stories and the application of wind loading. Where openings exist at a particular story, adjust the width of the wind pressure area.
be used to auto-generate the data necessary for the stories and the application of wind loading. Where openings exist at a particular story, adjust the width of the wind pressure area.
Once the floor diaphragm is defined in Story, the X-, Y-displacement degrees-of-freedom and the rotational degree-of-freedom about the Z-axis between all the nodes on the plane (plane parallel to the GCS X-Y plane) are constrained.
In addition, a part or all of the constrained nodes can be separated from the rigid floor diaphragm using Floor Diaphragm Disconnect.
-
Assign the wind load calculation standards in Wind Loads and enter the required data.
[Built-in wind load calculation standards in midas Gen]
Once the data required for the calculation of wind loads are defined, auto-calculate wind loads for each story in connection with the story data generated in Story. Use ![]() to verify the auto-calculated wind loads.
to verify the auto-calculated wind loads.
[Wind load generation...]
From the Main Menu select Load > Static Load > Lateral > Wind Loads.
Access Wind Loads to activate the dialog box defining the wind loads. Click ![]() to display the dialog box shown below.
to display the dialog box shown below.
 Load Case Name
Load Case Name
Select the load case name to be associated with the wind load. Click ![]() to the right to enter or modify new load cases.
to the right to enter or modify new load cases.
 Wind Load Code
Wind Load Code
Select the standards to be applied to the wind load calculation.
IBC 2012 (ASCE7-10): International Building Code 2012
IBC 2005 (ASCE7-05): International Building Code 2005
IBC 2000 (ASCE7-98): International Building Code 2000
UBC (1997): UBC 97 standards
ANSI (1982): ANSI standards
NBC (1995): National Building Code of Canada
Eurocode-1 (2005): Basis of Design and Actions on Structures
Note. Available National Annexes are as follows:
Recommended
Singapore
Eurocode-1 (1992): Basis of Design and Actions on Structures
BS6399 (1997): British Standard 6399 Loading for buildings
IS875(1987): Indian Standard
Taiwan (2002): Taiwan Building Code
NSR-10: Colombian Earthquake Resistance Building Code Ultimate Strength Design
(available upon request)
Japan (Arch, 2004): Loading Specifications and Commentaries for Buildings
Japan (Arch, 2000): Loading Specifications and Commentaries for Buildings
Japan (1987): Loading Specifications and Commentaries for Buildings
KBC (2009): Korea Building Code 2008
Korean (Arch, 2000): Buildings loading criteria and commentaries
Korean (Arch, 1992): Regulations related to structural criteria for buildings
China (GS50011-2001): Code for Seismic Design of Building
 Description
Description
Enter a short description.
 Wind Load Parameters
Wind Load Parameters
Enter the parameters to be applied to the wind load calculation.
 Wind Load Direction Factor
Wind Load Direction Factor
Enter the loading direction and the magnitude of wind load to be applied.
X-Dir.: Scale factor to be applied in GCS X-direction
Y-Dir.: Scale factor to be applied in GCS Y-direction
Z-Rot.: Scale factor to be applied in torsion about GCS Z-direction
Note
It is activated only when Japan (Arch, 2004) is selected.
 Additional Wind Loads
Additional Wind Loads
Enter additional wind loads that the auto-calculation does not take into account.
Press ![]() to enter the stories to apply additional wind loads and the magnitudes for each direction.
to enter the stories to apply additional wind loads and the magnitudes for each direction.
![]() : Display Tables and Graphs in a spreadsheet form for each loading direction and component of the auto-calculated wind loads.
: Display Tables and Graphs in a spreadsheet form for each loading direction and component of the auto-calculated wind loads.
Component: Assign the wind loading direction for a graphic display
Select Profile: Select the items to be displayed
Story Force
Story Shear
Overturning Moment
![]() : Display a spreadsheet Text Output file showing the wind load calculation process.
: Display a spreadsheet Text Output file showing the wind load calculation process.
Text Editor is automatically executed.
![]() : Apply the auto-calculated wind loads to the model.
: Apply the auto-calculated wind loads to the model.
Note
Refer to the relevant code for details regarding the wind load calculation.