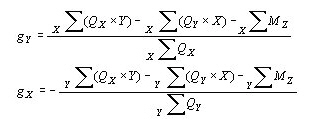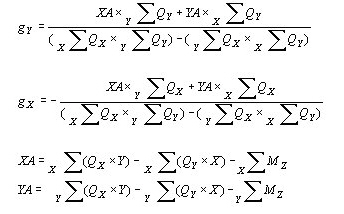Building Control Data
When the analysis model is a building, specify the ground level that will be referenced during the auto-generation of wind loads and equivalent static seismic loads according to the building codes. Also, specify whether to consider the entered mass components under the ground level for the eigenvalue analysis.(Refer to "Wind Load", "Static Seismic Load")
From the Main Menu select Structure > Building > Control Data > Control Data.
 Use Ground Level
Use Ground Level
Specify whether to consider the ground level during the auto-generation of the lateral forces applied to the model.
Ground Level
The ground level is expressed in terms of the coordinate in GCS Z-axis. The wind loads are automatically calculated for the superstructure above the Ground Level. The base shears of equivalent static seismic loads are also calculated at the Ground Level below which weight components are not considered.
 Consider Mass below Ground Level for Eigenvalue Analysis
Consider Mass below Ground Level for Eigenvalue Analysis
Specify whether to reflect the masses below the ground level in the Eigenvalue analysis.
If the option is not selected, the masses below the ground level are not considered.
 Story Shear Force Ratio of Member
Story Shear Force Ratio of Member
Specify whether or not to output distribution ratios of Story Shear Forces.
Note
Default has been changed from "Check Off" to "Check On".
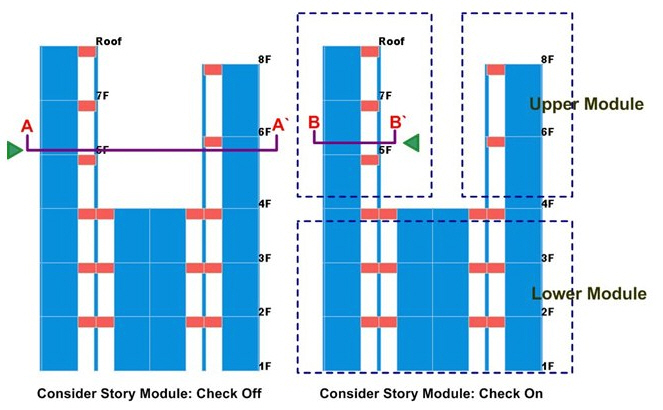
 Consider Story Module
Consider Story Module
Select a way of producing story shear force. (Refer to Note 1 and 2.)
 Consider Wind and Seismic Loads for Flexible Floors
Consider Wind and Seismic Loads for Flexible Floors
Static wind and seismic loads are applicable to the floors for which floor diaphragm is not considered.
 Eccentricity Ratio
Eccentricity Ratio
Note
Please refer to Note Eccentricity Ratio in Results > Result Tables > Story > Story Eccentricity.
Story Center (Mass/Load)
Specify the method of calculating Story Center, which will be used to calculate Eccentricity Ratio.
Use Mass: Use mass distribution to find story center
Use Axial Force: Use the axial forces resulting from static loads (long term loads) to calculate the story center. Multiple static loads can be applied simultaneously.
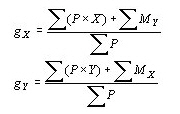
Where,
![]() : X, Y coordinates of the center (GCS)
: X, Y coordinates of the center (GCS)
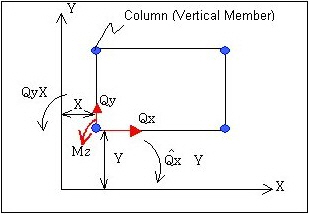
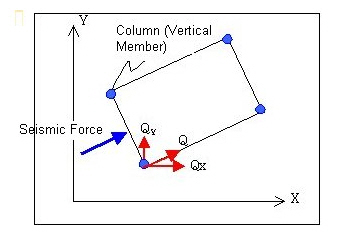
p: Axial force (for vertical columns), Vertical direction of shear force (for inclined columns)
X, Y: X, Y coordinates of vertical member (column head coordinates for inclined columns)
![]() , : Column head moments (GCS X, Y components)
, : Column head moments (GCS X, Y components)
For moments if a cantilever exists at a building corner/end
Use Shear Force: Use the shear forces resulting from static seismic loads to calculate the story center. The static seismic loads are applied in the GCS X and Y directions.
Note. Two methods depending on the story shear force directions
Story Stiffness Center
Select load cases, which will be applied to calculate the story stiffness center for calculating eccentricity ratios. Each of these load cases is assumed to be parallel with GCS X, Y axes. The stiffness is also calculated on the basis of load cases, which are not parallel with X, Y axes in which cases a warning message is generated.
X-Directional Load: Select a load case, which will be used to calculate the story stiffness center relative to Y-axis.
Y-Directional Load: Select a load case, which will be used to calculate the story stiffness center relative to X-axis.
 Story Response of Time History Results
Story Response of Time History Results
Select the option to produce the story results due to time history analysis (Results > Time History Results > Story Graph > Story Displ/Vel/Accel).
Story Center
Produce the Story Displ/Vel/Accel results for Story Center using the method selected from Story Center(Mass/Load).
Story Average
Calculate the Story Displ/Vel/Accel results averaging the story results of each vertical member. This option can be used when Story Center is not calculated (Eccentricity Ratio option is not used) or when Story Diaphragm is not assigned.