 Show/Hide
grid Show/Hide
grid
Show or hide the grid on the screen.
 Show/Hide
Datum Axis/Plane Show/Hide
Datum Axis/Plane
Show or hide the datum axis/plane on the screen.
 Show/Hide
WCS Show/Hide
WCS
Show or hide the WCS on the screen.
The WCS (Work-plane Coordinate System) is the coordinate
system of the work-plane. Work-plane is user-defined plane
to facilitate modeling
 Show/Hide
GCS Show/Hide
GCS
Show or hide the GCS on the screen.
The GCS (Global Coordinate System) is the fixed global
coordinate system.

There
are two basic coordinate systems used in the GTX NX; The
Global Coordinate System (GCS) and the Work-plane Coordinate
System (WCS).
The GCS (Global Coordinate System)
is the fixed global coordinate system expressed in the
bottom right-hand corner using red (X-axis), green (Y-axis)
and blue (Z-axis) arrows.
The WCS (Work-plane Coordinate
System) is the coordinate system that moves with the work-plane
and can be found at the center of the work screen. Because
the work-plane is used for entering the 2-dimensional
coordinates of a shape, the WCS changes along with the
workplace. The absolute 3-dimensional coordinates are
necessary to create a shape in space, but in most cases
the only the relative coordinates such as the model length
are given. In this case, modeling can be done easily by
moving the work-plane to an appropriate position and then
entering the 2-dimensional coordinates (the XY plane on
the WCS).
Please note that when extruding
the geometric shape, the load/boundary conditions and
extrude direction follows the GCS.
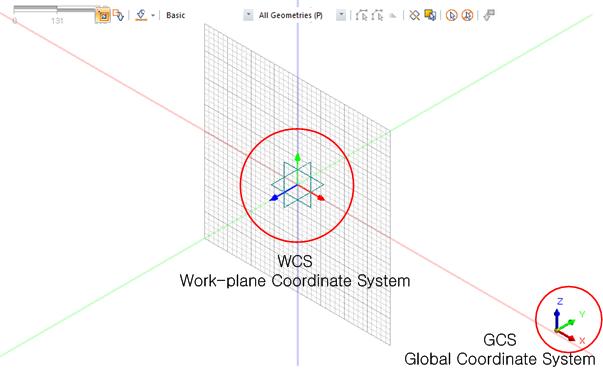
<Global
Coordinate System(GCS) and Work-plane Coordinate System(WCS)>

 Move
work plane Move
work plane
Move the work-plane to the desired location. This can
be done by [Reference plane], [3 point plane] or [Normal
direction] methods.
  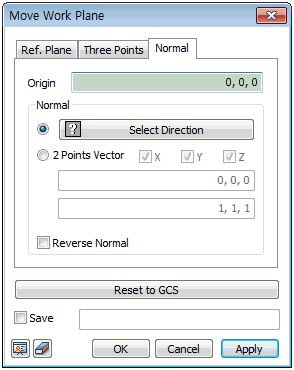
This function moves the current work-plane to the desired
location. This can be done by [Reference plane], [3 point
plane] or [Normal direction] methods.
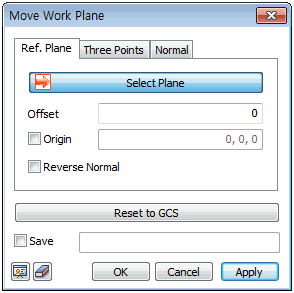
[Reference plane]: This function moves the grid
to a plane parallel to the reference plane. Clicking
the [Normal ] after moving the grid helps the
user work more easily. This function is convenient
when working on a plane different from the specified
work-plane.
GTS NX provides 7 basic work-planes: XY(0,0,1), XZ(0,-1,0),
XZ(0,1,0), YX(0,0,1), YZ(1,0,0), ZX(0,1,0), ZY(1,0,0).
If the workspace is a certain distance from the plane,
the user can specify the grid origin using the [Offset]
function.
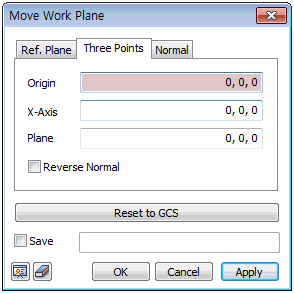
[3 point plane]: This function moves the work-plane
by selecting 3 points. The work-plane moves to the
plane define by the selected points, with the vector
created by the first and second points the X-axis
and the vector created by the first and third points
the Y-axis. [Normal direction]: This function moves the
work-plane by selecting a vector and a reference point.
The reference point is defined as the origin and the
normal direction to the vector is defined as the vertical
axis.
[Reverse Normal]
Reverse the vertical direction
(the Z-axis of the WCS) of the plane.
[Reset to GCS]
Return to the initial grid
position.
[Save]
Check the [Save] button and
enter a name to register the workplace under Work tree
> Workplane.

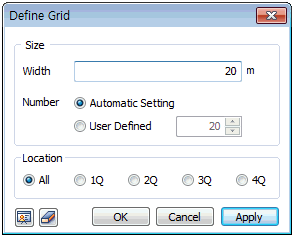
 Define
grid Define
grid
The grid is always located on the XY plane of the work-plane
to ease the modeling process. When modeling with the grid,
the grid snap ( ) function can be used
to specify the desired location and easily estimate the
approximate model or element sizes. ) function can be used
to specify the desired location and easily estimate the
approximate model or element sizes.
The grid setting can be set according to the convenience
of the user and the dimensions of the model.
 Define
snap Define
snap
The user can specify the location of the point using
various snap options shown in the table below.
Grid snap |
Positions
the mouse snap on a grid point in the
work-plane. |
Point snap |
Positions the mouse
snap on a point. |
End snap |
Positions the mouse snap on the
closest endpoint of an edge. |
Middle snap |
Positions the mouse
snap on the midpoint of an edge. |
Perpendicular snap |
Positions the mouse snap on the
perpendicular point of an edge. |
Center snap |
Positions the mouse
snap on the center point of a circle/arc. |
Quadrant snap |
Positions the mouse snap on the
four circle/arc quadrant points. |
Intersection snap |
Positions the mouse
snap on the intersection point between two edges. |
Tangent snap |
Positions the mouse snap on the
tangent point. |
Arbitrary snap |
Designates an arbitrary
snap. |
Node |
Positions the mouse snap on a
node. |

When using a snap related to
a particular edge, such as end snap or middle snap, the
user needs to position the mouse above the target edge
of the snap, rather than on the position of the target
(end, middle). |


