Map Mesh: Face

Function
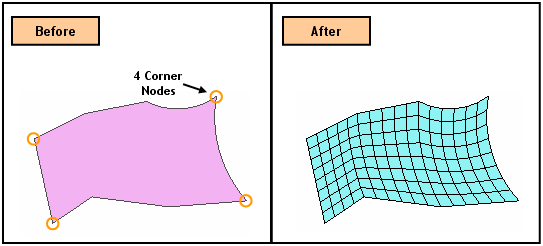
Map-Mesh Face generates mapped meshes on selected faces (Shell, Face).
Call
Mesh > Map Mesh > Face
<Map-Mesh Face>
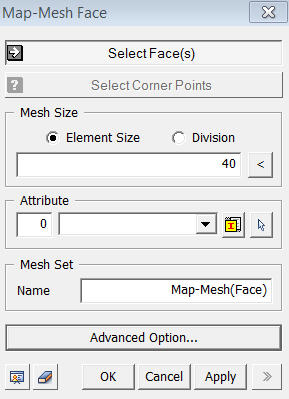
Select Face(s)
Select
Faces (Shell, Face), which will be
automatically meshed.
Select Corner Vertices
The
Mapped Mesh generating algorithm creates a square mesh by mapping a selected
shape into an imaginary square. It then maps the
generated mesh back to the original shape. Thus,
a group of four edges needs to be defined for mapping each edge of the
square. The edges of the face are manually grouped
into four edges by selecting four vertices of the edges composing the
boundary edges of the face.
Mesh Size
Element Size
Specify
the element size.
Division
Specify
the number of divisions at the boundary edges of the shape for a meshing
operation.
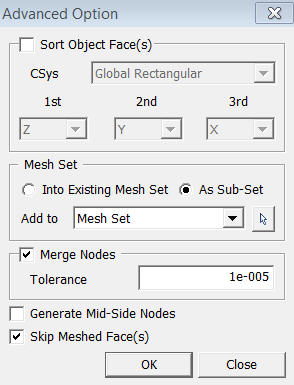
<Advanced Option>
Sort Object Faces
Specify
the order of Map Mesh generation. If Map Mesh is generated in multiple
Faces in a random order, it often fails due to unmatched number of seeding
between Faces. Therefore, defining the order will resolve it is recommended
to specify the order.
CSys
Choose the reference coordinate system between the Global Rectangular System and the Global Cylindrical System.
Global Rectangular
Sorts based on Global X, Y, and Z axis.
Global Cylindrical
Sorts based on Radius (R), Rotation (T), and Z-axis (Z).
Skip Meshed Face(s)
Does not generate mesh(es) for selected Face.
Notes
Mapped Mesh Algorithm
First, appropriate seeding is assigned to the face for which mapped mesh will be generated, and the corner vertices are assigned. The corner vertices are indicated as A, B, C and D in Fig (i). The seeding between the corners A & B and between the corners A & D are assigned 4 and 12 respectively.
The mapped mesh generating algorithm then maps the selected face into a square and generates a 2-D mesh reflecting the seeding as shown in Fig (ii). The mesh of the square domain is again mapped into the object domain as shown in Fig (iii).
A main reason for failing to generate a mapped mesh is attributed to unmatched division numbers of elements for cross-faced edges. In the above example, the number of divisions for the edge A-B and edge C-D is 4. Similarly, the division number is identical for the edges A-D and B-C. Otherwise, the rectangular meshing is not feasible in the square domain.
In cases where the mesh fails to generate, refer to Remove Edge.