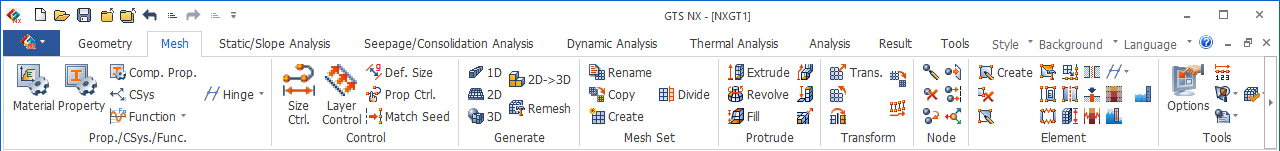
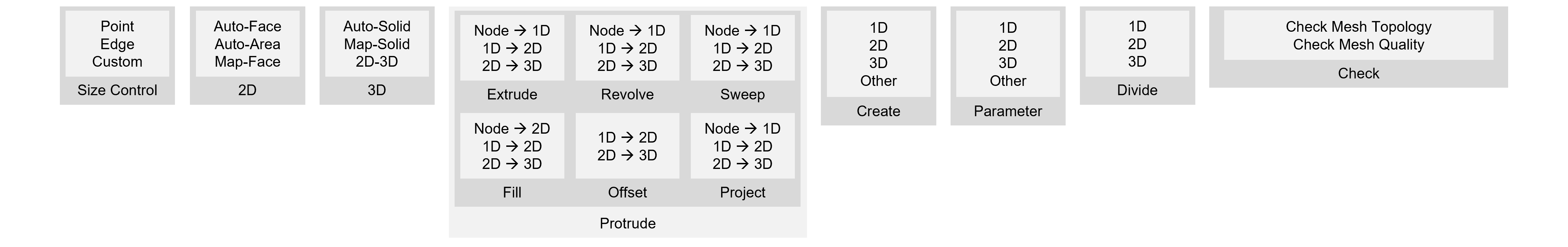
Define
the mesh size directly or input the number of
divisions for the surface forming edge to set
the mesh size. Assigned properties can be specified
during mesh creation, and the name of the mesh
set can be pre-determined.
Option
( ) )
Additional
options are provided depending on the mesh generation
method. The mesh shape, mesh density and generation
algorithm can be set. The initial settings take
into account the efficiency and accuracy depending
on the geometric shape for the best mesh generation.
The detailed settings are as follows.
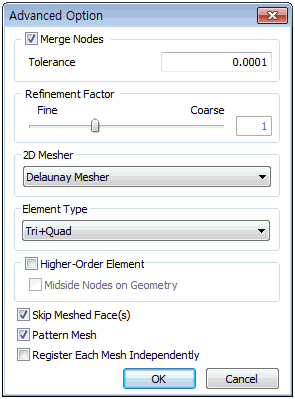
Merge Nodes
Merge 2 or more nodes within the tolerance during
mesh generation. Nodes separated by tiny gaps
are the main sources of error during analysis,
and small gaps within the tolerance can be automatically
joined for mesh creation.
Refinement Factor
Select the mesh size (mesh density) that will
be created in the interior of the selected shape.
A more compact mesh is created as the value approaches
[Fine]. Fine meshes provide more detailed result
analysis, but it is important to consider analysis
time and efficiency when selecting the mesh density.
2D Mesher
Select the mesh generation algorithm for mesh
generation. The user can select between three
options; Loop Mesher, Grid Mesher and Delaunay
Mesher. The generated shape and process change
with the selected algorithm.
Loop: Mesh generation method and shape
based on Looping algorithm Grid: Complex mesh generation based
on Modified grid algorithm Delaunay: Indirect mesh generation based
on Delaunay triangulation algorithm
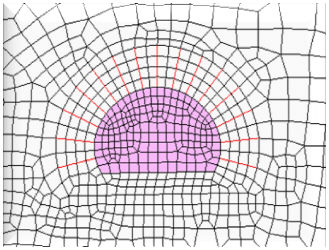 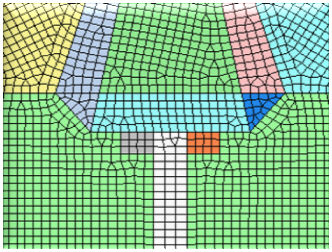 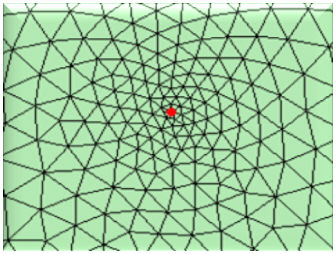
<Loop> <Grid> <Delaunay>
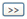
Element
type
Generate
a mesh with the selected shape. The user can select
between a triangle, quadrilateral or a combination
of the 2. Quadrilateral meshes provide a more
stable analysis, but for complex geometric shapes
where quadrilateral meshes are difficult to generate,
it is better to generate a triangular mesh.
Higher-Order
Element
Generate
another node between mesh nodes to create a higher
order mesh. Higher order adds a computation point
and therefore, a more detailed analysis is possible,
but the analysis time becomes longer. It is recommended
that meshes be created with reference to the mesh
shape and mesh density, and the higher order meshes
be created only when necessary, depending on the
analysis method. For example, generate a higher
order mesh for the strength reduction method on
a slope face where analysis of detailed deformation
sections is necessary.
Check the
[Skip Meshed Face(s)] to prevent overlapping generation
of meshes on a surface with an existing mesh.
The homogeneity option can be set to make the
mesh sizes as uniform as possible. Also, when
generating meshes on multiple surfaces at the
same time, the mesh sets can be individualized
by each surface or grouped into 1 mesh set. |