|
Eigenvalue analysis is used to analyze the inherent dynamic properties of the ground/structure, and this can be used to obtain the natural mode(mode shape), natural period (natural frequency), modal participation factor etc. of the ground/structure. These properties are determined by the mass and stiffness of the structure. In other words, if a structure is determined, the natural frequency and vibration mode (natural mode) are also determined and the number of properties are the same as the degree of freedom of the structure. For real cases, the structure does not vibrate at a single mode shape and multiple modes overlap to display a complex vibration shape.
Here, the Mass participation factor is a mass percentage factor that represents how much of the structure participates in the vibration for each vibration mode when the structure is vibrated at a complex vibration mode. For example, if the first mode mass participation factor is 60%, 60% of the total mass of the structure participates in the first mode. Hence, the a mode with a high mass participation factor is considered in the earthquake wave for analysis.
For general structure, considering only vibration modes with a mass participation factor sum of around 90% is still regarded as a sufficiently accurate analysis. However, the ground material properties are relatively smaller that structural properties and it is hard to have a mass participation factor of 90% in Eigenvalue analysis. The period is also relatively smaller and no specific standard exists.
Natural periods are defined as the time taken for a structure to vibrate from its natural vibration state to the particular mode shape using a natural value that 1:1 corresponds to the natural mode.
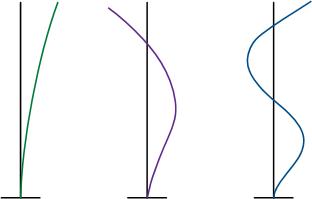
<Natural mode shapes>
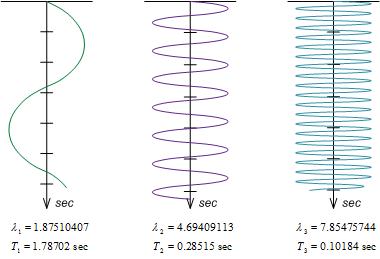
<Natural frequency>
The General seismic design criteria requires that each mode’s effective model mass included in the analysis should retain more than 90% of the total mass. This is to include most of the major modes that influence the result.
|
