|
Is a material that simplifies complex nonlinear behavior of geo-material properties into equivalent linear properties and allows ground-structure analysis under dynamic loading. Shear strain due to earthquakes or other dynamic loading is constantly changing and the effective shear strain concept is used to set an equivalent linear value. The required input parameters and application process are as follows.
|
Process
|
Analysis process
|
|
1
|
Assume initial Shear modulus and damping ratio
|
|
2
|
Compute ground response and strain hysteresis from initial values
|
|
3
|
Use maximum strain from computed strain hysteresis to calculate effective strain
|
|
4
|
Use equivalent linear damping ratio corresponding to effective strain and Shear modulus to re-compute the ground response and strain hysteresis
|
|
5
|
Repeat process 2~4 until the calculated Shear modulus and damping ratio error variation is within the tolerance
|
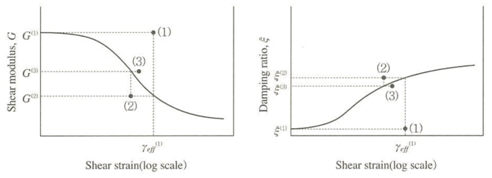
<Convergence of nonlinear Shear modulus and damping factor using the equivalent linear method>

The stress-strain relationship graph for equivalent linear analysis and nonlinear analysis can be expressed as follows.
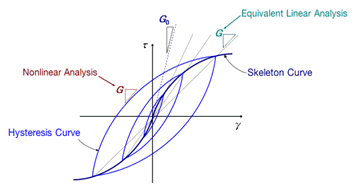
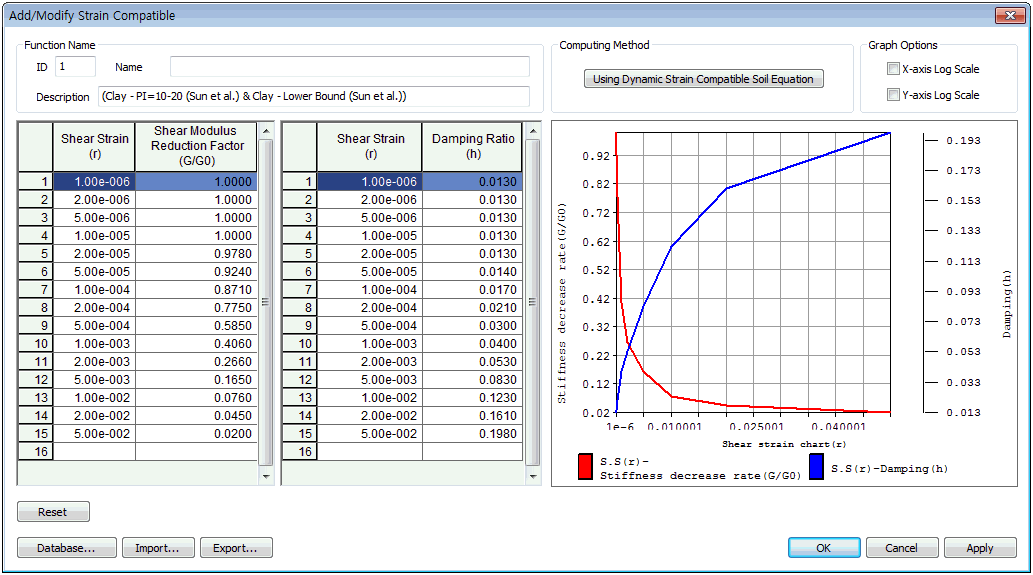
In the equivalent linear method, the nonlinear characteristics of the geo-material can be expressed as a function of the ratio of maximum shear modulus 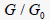 and shear modulus and shear modulus 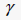 and shear strain , and a function of damping ratio and shear strain , and a function of damping ratio 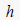 and shear strain and shear strain 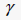 . These material properties can be found from the dynamic strain test as shown below. . These material properties can be found from the dynamic strain test as shown below.
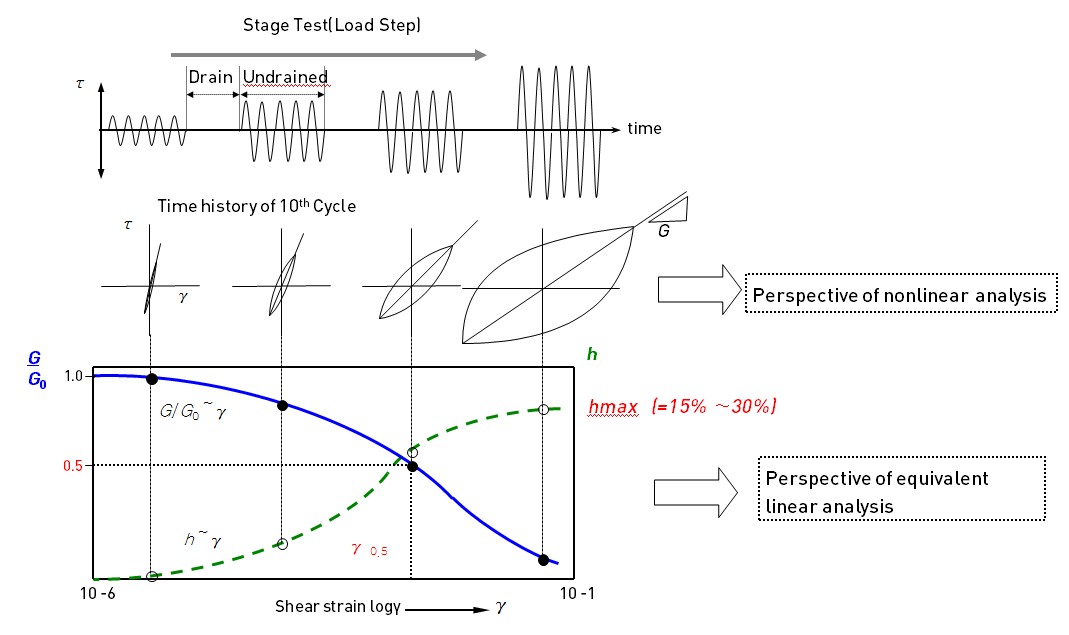
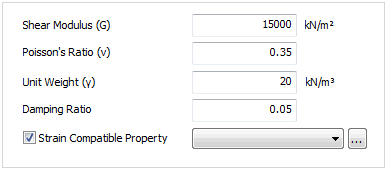
Strain compatibility properties can be set using a function of Shear modulus and damping ratio to strain when considering the nonlinear, inelastic behavior of the ground. If the function is not defined, the geo-material is assumed to be linear and an entered (fixed) Shear modulus and damping ratio is used in the analysis. Various DB exist for each type of ground. Refer to 'Function' section for more detailed information.
|
