Natural ground is generally
layered and sloped, making it possible to have different
strengths in each orthogonal direction. The figure below
shows a soil layer with an angle between the
global x axis and the element x' axis and displays perpendicular
anisotropy (orthotropy) with the x' axis and z' axis of
the element.
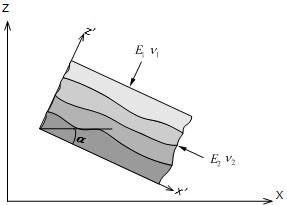
<Orthotropic
model>
This
orthotropy is simulated by assigning different stiffness
to the tangent and normal direction to the stratification
(fault) orientation. Generally, the normal direction stiffness
decreases in comparison to the tangential stiffness and
the anisotropic shear strength is defined by the Shear
modulus (G). For fully isotropic case, 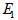 , , 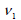 is equal to is equal to
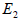 , , 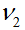 respectively and G is defined by
respectively and G is defined by 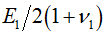 . .
Transversely
isotropic materials are material models defined by an
isotropic transverse section with a vertical axis to the
section. The physical properties are the same within the
transverse section and the vertical direction has different
properties.
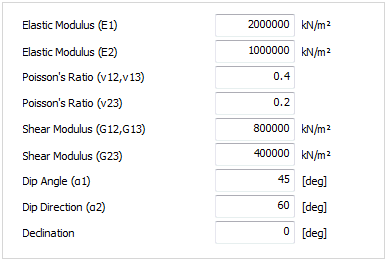
Here,
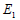 is the Elasticity modulus in the
vertical axis to the section, is the Elasticity modulus in the
vertical axis to the section, 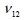 , ,
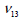 and and 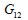 , , 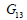 are the
Poisson’s ratio and Shear modulus of the surfaces generated
by the vertical and section with the other axes respectively. are the
Poisson’s ratio and Shear modulus of the surfaces generated
by the vertical and section with the other axes respectively.
The
local coordinate system is defined by the dip angle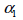 and dip direction and dip direction 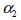 .
Because the reference axis of the inclined plane and horizontal
plane ( .
Because the reference axis of the inclined plane and horizontal
plane ( 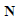 and and
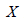 respectively) are not identical,
use the auxiliary angle respectively) are not identical,
use the auxiliary angle 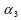 that subtracts
the declination (angle formed between the 2 axes) from that subtracts
the declination (angle formed between the 2 axes) from
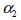 when setting the actual transformation
matrix. when setting the actual transformation
matrix.
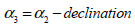
Thermal

Conductivity: the ability to conduct thermal
energy.
Specific Heat: the amount of heat required to raise single
unit mass of a substance by single temperature unit. (required
for transient heat transfer problems)
Heat Generation Factor: the value of the heat load
multiplied by the exothermic coefficient used as the load
vector for heat transfer analysis is the total exothermic
load applied to the object. |
