Input
the surface inflow/outflow rate of a specific point in
terms of flow rate per unit area. It can be defined as
either an [Edge Flux] or [Face Flux]. Generally, the [Edge
Flux] is input for 2D models and [Face Flux] is input
for 3D models.
The
Face flux can be defined by entering the value on the
edge or surface geometry, or directly entering it on the
selected element edge.
Define
the inflow input from rainfall etc. as a (+) value and
define the outflow input from excavation or pumping etc.
as a (-) value.
Transient
analysis (where the water level changes with time) can
be defined as a [Function].
When
using a function, the input value and function value are
multiplied and reflected in the analysis.
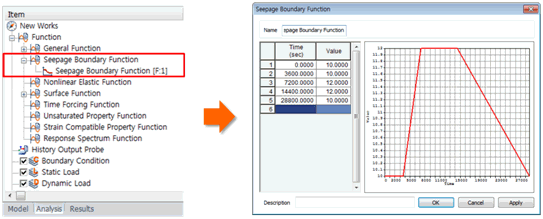
The
defined function is registered under Function > Seepage
Boundary Function, and can be edited as a table using
the right mouse click > Edit.
Rainfall Data
can be inputted into GTS NX in the form of Surface Flux,
this can be also be extended to certain nodes in case
if a small portion is considered instead of total area.
The application of rainfall data as surface flux is illustrated
below:
Amount of Rainfall - 100 mm/hr
~ 0.028 mm/sec ~ 2.8e-5 m/sec
The
flux data input is discharge per unit area can be interpreted
as Q/m2 ( Discharge Q = m3/sec), when Q is divided
per unit area, it gives the height of the rain column
that is falling in that area as post application of dimensional
analysis, the flux input becomes m/sec. Hence, you can
enter the rainfall data as described before directly as
2.8e-5 m/sec. The distance inputs can also be changed
into mm or cm and the time inputs into hours or days.
Using the seepage boundary function, one can
also enter the rainfall data distribution as available
from the meteorological data.
If q > Ksat, then Total Head
= Pressure Head
The
flux-head boundary conversion condition for rainfall analysis.
For
example, the Surface flux can be used to define the ground
surface boundary conditions when the rainfall intensity
on the ground surface is inputted.
This
function applies a forced inflow rate, as large as the
rainfall intensity, onto the ground surface. If the absorption
capability of the soil stratum surface is larger than
the rainfall intensity, the soil stratum absorbs all the
rain water. However if the absorption capability is smaller,
rain is absorbed into the ground surface by only the absorption
capability amount, and the rest of the rain flows across
the ground surface.
If
the rainfall intensity is larger than the absorption capability,
the ground surface is in a saturated state during rainfall,
as if the groundwater level existed above the surface.
Hence, the area of rainfall needs to be changed to a water
level line.
Use
the [If q > Ksat, then Total Head = Pressure Head]
option to automatically change the ground surface boundary
from the existing rainfall intensity inflow condition
to a water level condition for analysis. This option is
only available when the rainfall intensity acting on the
surface is larger than the absorption capability of the
ground surface.
Boundary Set
Register
the set constraint conditions on the desired boundary
set. The user can specify the name of the boundary set
or create a new boundary set for the recently entered
data values. |