Create
Add a ground or structure material. The following
4 material types can be selected and the model
type can be set for each material type.
The model type available for each material type
is shown below. The ground/structure material
properties and the material behavior properties
are defined for each model type. Here, the elements
used for ground modeling such as plane strain
or solid can be assigned to a structure material
that does not consider Ko effects or permeability
properties.
Material
type |
Model type |
Ground
material |
Structure
material |
Material
behavior properties |
|
|
|
O |
O |
Linear elastic |
|
O |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
X |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
X |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
X |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
X |
Nonlinear
elastic |
|
O |
X |
Nonlinear
elastic |
|
O |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
X |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
X |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
X |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
X |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
X |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
X |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
X |
Elasto-plastic |
|
O |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
Concrete
Smeared Crack |
X |
O |
- |
Concrete
Damaged Plasticity |
X |
O |
- |
Masonry |
X |
O |
- |
Orthotropic |
|
O |
O |
Linear elastic |
|
O |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
X |
O |
Linear elastic |
|
X |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
2D
Equivalent |
|
O |
O |
(Equivalent) Linear
elastic |
Interface
/ Pile |
|
X |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
X |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
X |
O |
Elasto-plastic |
|
X |
O |
Nonlinear
elastic |

Isotropic
Isotropic materials have the same properties
in every direction and is used to define material
behavior properties of most linear-elastic / nonlinear
elastic / elasto-plastic materials.
Orthotropic
Natural ground is generally layered and sloped,
making it possible to have different strengths
in each orthogonal direction. This option can
also be used to define Jointed Rocks, which have
different properties depending on the direction
and behave differently according to the specific
confinement conditions. In case of 2D Orthotropic, users
can define different values of stiffness along
each direction. It is required to define geometrically
orthotropic with significant different stiffness
in horizontal and vertical direction.
2D Equivalent
2D equivalent linear analysis specific model.
Use the converging strength and damping ratio
from the equivalent linear method to consider
the nonlinear and n1lastic behavior of materials.
Interface / Pile
Applied when simulating relative behavior (interface
behavior) between ground and structure.
Modify/Copy/Delete
Modify the parameters of an added material.
Copy can be used when adding multiple materials
while only changing certain parameters.
Import/Import from
Excel / Export to Excel
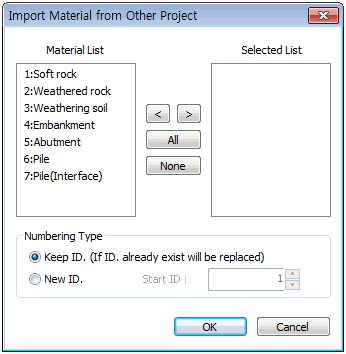
Import the material properties from a different
model file with a saved material/property. This
operation is useful when analyzing the existing
project under the same conditions. Selecting the
import file generates the material list containing
all saved materials. The user can select the desired
material.
The user can construct the frequently used material
DB by importing or exporting the excel file containing
the material properties.
Renumber
Change the registration number of a material.
Repeating Add/Delete automatically sets the registration
number to recently added number+1.
Refer to Ch.4 of the Analysis manual to understand
the Finite element formulization and yield shape.
The input parameters and behavioral characteristics
for each material model are as follows. |
