 Revision of Ver.7.4.1
Revision of Ver.7.4.1 Revision of Ver.7.4.1
Revision of Ver.7.4.1Function
Story is used to define the floor levels if the analysis model is a building. Because the positions of the stories are defined using the GCS Z-axis coordinates, the floor planes of the building must inevitably be parallel to GCS X-Y plane.
Story is used for the following purposes:
Assign wall combination numbers to the wall elements entered in the analysis model.
Define stories to apply the auto-calculated lateral forces as story forces. (Refer to "Wind Load" and "Static Seismic Load")
Consider automatically rigid diaphragm action and specify diaphragm masses at the relevant stories. (Refer to "Floor Diaphragm Masses")
After analysis, Story is used to classify and arrange results data such as story drifts, input loads and self-weights by stories. (Refer to "Story Drift", "Story Weight Table", "Story Load Table")
 Revision of Ver.7.4.1
Revision of Ver.7.4.1Data entry and results data related to Story
In general, stories are identified by floors in a building. In generating an analytical model for a building structure, floors are considered as rigid diaphragms, and lateral loads such as wind and seismic loads are assumed to act on the floor diaphragms. Also in design of the building structure, results related to Story are required, which are story stiffness ratios, story eccentricity ratios, story drifts, story shear forces, etc.
1. Auto generation of story data
Midas Gen provides the auto-generation function for story data by automatically recognizing the z-coordinates of nodes in the structure. (In the main menu, Model > Building > Story)
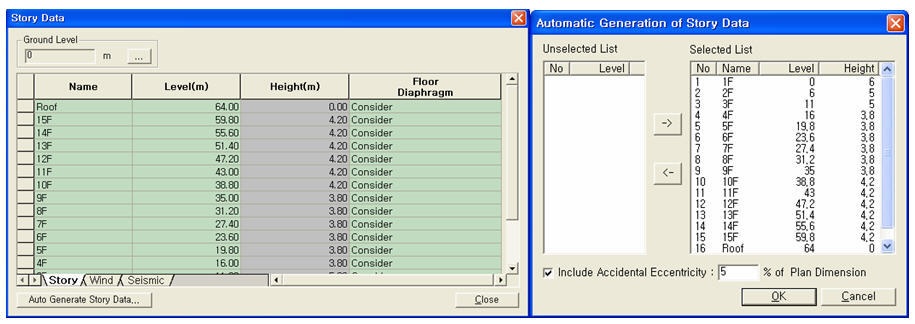
Auto-generated story data
If the user defines the Ground Level, basements can be considered to which auto-generated wind and seismic loads are not applied. Floor diaphragms are automatically considered for all floors except for the lowest level. In order to release the floor diaphragms for specific stories, select Model>Boundary>Disconnect Diaphragm in the main menu.
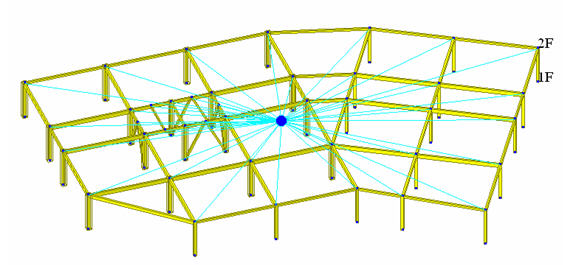
Display of story diaphragm
2. Check the results related to story
Midas Gen provides the following results:
Story drift
Story drift (Time history analysis)
Story Displacement
Story shear force (Response Spectrum Analysis)
Story shear force (Time History Analysis)
Story mode shape
Story eccentricity
Story shear force distribution ratio
Torsional amplification factor
Overturning moment
Story axial force sum
Stability coefficient
Torsional Irregularity
Stiffness Irregularity Check
Weight Irregularity Check
Capacity Irregularity Check
Ultimate Story Shear Check (In Taiwan version only)
Story shear force distribution ratio can be produced when Story Shear Force Ratio (Model>Building>Control Data) is checked on before analysis is performed.
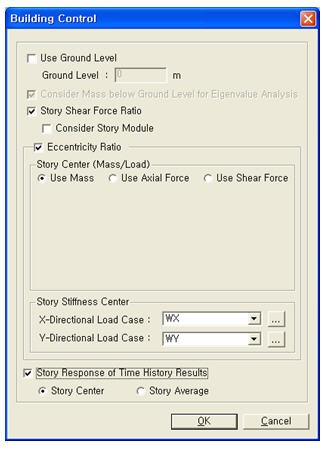
Calculation methods for Story Center
Call
From the Main Menu select Model > Building > Story.
Select Geometry > Building > Story in the Menu tab of the Tree Menu.
Shortcut key: [F10]
Entry
Use the Table Entry function to directly
enter the story data in the Table or click .jpg) .
.
.jpg)
The ground level is expressed by the coordinate of the GCS Z-axis. The stories from the Base to the ground level are assumed as underground stories and designated as 'B1', 'B2'... during the auto-generation of story data.
Refer to "Usage
of Table Tool" in the Story Entry Table to enter the following
data:
Basic directions (Cell motion, selection, size control, etc.)
Data manipulation (Add, delete, modify data, etc.)
Copy/Paste data using clipboard
Supplementary functions by Table types
The command supplies 3 Table dialog boxes related to stories and the data entries for each dialog box are as follows :
Name : Story name
Level : Story height (elevation)
Height : Floor to floor height
Floor Diaphragm : Assign Floor Rigid Diaphragm to the relevant story. This function constrains Dx, Dy and Rz to the relevant story.
Note 1
If “Do not consider” is selected for Floor Diaphragm and Membrane Type of wall is defined, Singular Warning message is displayed when the analysis is carried out. This is because Membrane Type of wall does not have out-of-plane stiffness. It can be resolved by changing the Membrane Type into Plate Type.
Note 2
If Floor Diaphragm is considered, all masses of the relevant story are lumped into Mass Center. The mass data lumped into Mass Center can be checked from Query> Story Mass Table.
Note 3
When a Support condition (3 translational degrees of freedom and 3 rotational degrees of freedom restrained) is assigned to a certain node on Floor Diaphragm, the degrees of freedom overlapping with Floor Diaphragm are automatically released.
Note 4
In case of stepped slabs, consider Floor Diaphragm to each slab and define Elastic Link-Rigid Type to the slab gap.
Name : Story name
Floor Width X-Dir. : Effective width of the building in X-axis, subjected to GCS Y-direction wind load
Floor Width Y-Dir. : Effective width of the building in Y-axis, subjected to GCS X-direction wind load
Floor Center Xc : Coordinate of the position in GCS X-direction, to which the wind load is applied
Floor Center Yc : Coordinate of the position in GCS Y-direction, to which the wind load is applied
Name : Story name
Eccentricity
X - Dir.
Accidental eccentricity distance in X-direction to calculate the accidental
eccentricity moments due to the seismic loads at each story in GCS Y-direction
when the equivalent static seismic load is calculated
Eccentricity
Y - Dir.
Accidental eccentricity distance in Y-direction to calculate the accidental
eccentricity moments due to the seismic loads at each story in GCS X-direction
when the equivalent static seismic load is calculated
Click .jpg) to auto-generate the
story, wind and seismic table data using the geometric data of the building.
to auto-generate the
story, wind and seismic table data using the geometric data of the building.
Note
MIDAS/Gen auto-generates story data based on the entered nodal coordinates.
MIDAS/Gen assumes the Z-coordinates of all the entered nodes as story levels
and includes them in the Selected List. Click .jpg) before clicking
before clicking
.jpg) to exclude the levels not required from the Selected
List and move to the Unselected List.
to exclude the levels not required from the Selected
List and move to the Unselected List.
.jpg)
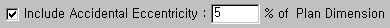
When a static seismic load needs to be automatically calculated, check on the box to consider Accidental Eccentricity for torsional moment. The magnitude of the eccentricity is specified in percentage relative to a Plan Dimension.